- An ideal Carnot heat engine is operating between temperatures Thigh and Tlow, where Thigh is the highest temperature that occurs within the piston during one cycle, and Tlow is the lowest. Which of the following formulas correctly gives the efficiency that such an engine has for converting input heat to output work? (Both temperatures must be stated in kelvins.)
- efficiency = (1 + Thigh/Tlow) × 100%
- efficiency = (1 + Tlow/Thigh) × 100%
- efficiency = (1 − Thigh/Tlow) × 100%
- efficiency = (1 − Tlow/Thigh) × 100%
- Helium gas can be found in a balloon, but at low temperatures it can be in other phases.
Which of the following phases of matter for helium will have the highest entropy?
- solid
- liquid
- semi-liquid
- gas
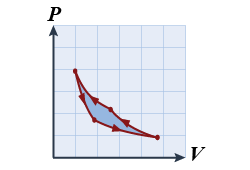
- In the pressure–volume diagram shown, what kind of thermodynamic process is depicted?
- a refrigerator
- a heat engine
- a Carnot cycle
- an adiabatic isotherm
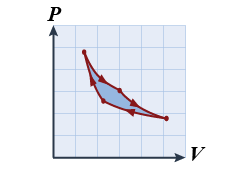
- For one complete cycle plotted in the PV diagram shown, which of the following statements is correct?
- No net work is done during the cycle.
- Net work is done on the gas during the cycle.
- Net work is done by the gas during the cycle.
- The gas increases its temperature.
| | - Which statement best describes how a refrigerator works?
- It uses energy to cause heat to flow from a colder location to a hotter location.
- It does work by causing heat to flow from a hotter location to a colder location.
- It cools through reverse osmosis.
- It rejects heat from the environment into the enclosure.
- Which one of the following SI units (labels) could properly describe the product of pressure and volume?
- newton (N)
- joule (J)
- watt (W)
- horsepower (hp)
- Which sentence best describes the following thermodynamics equation?
- The change in speed is always greater than or equal to zero.
- Entropy does not change.
- The change in static energy for a heat engine is greater than or equal to zero.
- Total entropy only increases or stays the same.
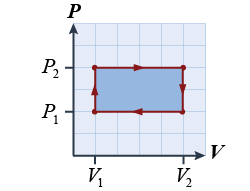
- For one complete cycle of the thermodynamic process shown in the illustration, which is the equation for the work done by the gas?
- (P1 − P2) / (V1 − V2)
- (P2 − P1) / (V2 − V1)
- (P1 − P2) × (V1 − V2)
- (P2 − P1) × (V2 − V1)
- Imagine that 100 J of thermal energy spontaneously moved from cool air (at 20°C) to a warm cup of tea (at 60°C). Which of the laws of thermodynamics, if any, would this process violate?
- the first law of thermodynamics only
- the second law of thermodynamics only
- both the first and second laws of thermodynamics
- none of the laws of thermodynamics
|

