- What happens to the internal energy of a system if it does work on something else?
 The hot coffee in a mug cools from 80°C to room temperature over the course of 15 minutes. An equal amount of hot coffee, also at 80°C, in an insulated travel mug cools to room temperature over the course of 4 hours. In which mug did the coffee experience a greater change in entropy? The hot coffee in a mug cools from 80°C to room temperature over the course of 15 minutes. An equal amount of hot coffee, also at 80°C, in an insulated travel mug cools to room temperature over the course of 4 hours. In which mug did the coffee experience a greater change in entropy?
- Describe what an adiabatic process is for a gas.
- Describe what an isothermal process is for a gas.
- What is the difference between a heat engine and a heat pump? Give one example of each.
- Imagine that the gas within a piston expands, pushing against an outside pressure. Which of the following statements are correct? (There may be more than one right answer.)
- The gas within the piston does positive work on its surroundings.
- The gas within the piston does negative work on its surroundings.
- The surroundings do positive work on the gas within the piston.
- The surroundings do negative work on the gas within the piston.
 Which statement is consistent with the following equation for a Carnot cycle? Which statement is consistent with the following equation for a Carnot cycle? - The efficiency of a Carnot engine is equal to the ratio of the two temperatures it is operating between.
- No Carnot engine with T1 above absolute zero can be 100% efficient.
- When the upper and lower temperatures of a Carnot engine are very close to each other, then it will have nearly 100% efficiency.
- By inverting the operating temperatures, a Carnot engine can operate at >100% efficiency.
 Mirette put together a business model for a company that would build ideal Carnot engines that convert 100% of the input heat into energy. Would it be a good idea to invest your life savings in her company? Mirette put together a business model for a company that would build ideal Carnot engines that convert 100% of the input heat into energy. Would it be a good idea to invest your life savings in her company?
| |
- The gas within a piston expands from an initial volume of 25 mL to a larger volume of 125 mL, against a constant pressure of 100,000 Pa (approximate atmospheric pressure at sea level). How much work does the gas in the piston perform?
- A bearded dragon lizard basks in the desert Sun during the day and reaches a body temperature of 40°C. At night the air temperature quickly becomes 15°C. During the course of the night the lizard loses 100 J of heat while his body temperature equilibrates to the nighttime air temperature. What is his change in entropy?
 A hot rock is plucked from a fire pit and dropped into a bucket of cold water. The rock has a temperature of 80°C, and it transfers an initial 500 J of thermal energy to the water. Assume that the temperatures of the rock and water remain unchanged during this first instant. A hot rock is plucked from a fire pit and dropped into a bucket of cold water. The rock has a temperature of 80°C, and it transfers an initial 500 J of thermal energy to the water. Assume that the temperatures of the rock and water remain unchanged during this first instant.
- Does the entropy of the rock increase or decrease? By how much?
- Does the entropy of the water increase or decrease? By how much?
- Does the total entropy of the rock+water system increase or decrease? By how much?
 Suppose that an internal combustion engine operates between an internal temperature of 2,000 K and an exhaust temperature of 1,000 K. What is the engine’s maximum theoretical efficiency expressed as a percentage? Suppose that an internal combustion engine operates between an internal temperature of 2,000 K and an exhaust temperature of 1,000 K. What is the engine’s maximum theoretical efficiency expressed as a percentage?
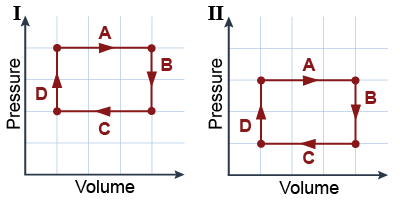
 These two PV diagrams each depict one thermal cycle of a piston containing an ideal gas. The pistons are physically identical, but Piston I operates at higher pressure, on average, than Piston II. The lower-left corner of the coordinate grid represents the origin (zero pressure and volume). These two PV diagrams each depict one thermal cycle of a piston containing an ideal gas. The pistons are physically identical, but Piston I operates at higher pressure, on average, than Piston II. The lower-left corner of the coordinate grid represents the origin (zero pressure and volume).
- Which piston does more (positive) work during the expansion phase (I, II, or a tie)?
- Which piston does more (negative) work during the contraction phase (I, II, or a tie)?
- Which piston does more (positive) work during one complete cycle (I, II, or a tie)?
|

