- Consider the range equation.
- If the velocity doubles, what effect does this have on the range?
- Explain how the equation describes the range at angles of 0º and 90º.
 Why is white paper (e.g., from a roll of white craft paper) placed underneath carbon paper when conducting a trajectory experiment with a falling marble, as in Investigation 6B on page 186? Why is white paper (e.g., from a roll of white craft paper) placed underneath carbon paper when conducting a trajectory experiment with a falling marble, as in Investigation 6B on page 186?
 You and your lab partner are given a marble and a trajectory apparatus ramp that acts as a marble launcher. You will compete with other lab groups to see who can launch their marble the furthest. With what projection angle should you set up the end of your marble launcher ramp? You and your lab partner are given a marble and a trajectory apparatus ramp that acts as a marble launcher. You will compete with other lab groups to see who can launch their marble the furthest. With what projection angle should you set up the end of your marble launcher ramp?
 What are the advantages of using real-time technology to generate graphs of motion (position–time or velocity–time graphs) down an inclined plane over how Galileo collected his data? What are the advantages of using real-time technology to generate graphs of motion (position–time or velocity–time graphs) down an inclined plane over how Galileo collected his data?
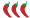 The figure above depicts a marble on a launch ramp that strikes a vertical, movable target. The carbon paper leaves a mark on the target each time a marble hits it. Describe how you would use this trajectory apparatus to graph the shape of the marble’s trajectory after it leaves the launch ramp. The figure above depicts a marble on a launch ramp that strikes a vertical, movable target. The carbon paper leaves a mark on the target each time a marble hits it. Describe how you would use this trajectory apparatus to graph the shape of the marble’s trajectory after it leaves the launch ramp.
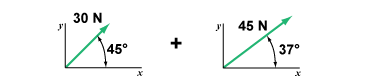
- What is the net force that is the result of combining a 30 N force at a 45° angle above the horizontal and a 45 N force 37° above the horizontal?
- At what angle is a force directed if its horizontal component is 10 N and the vertical component is 15 N?
- What is the range of magnitudes that can be attained from the combination of forces with magnitudes of 7 and 5 N?
| | - What is the resultant of the following calculation adding two vectors: where = (a, b) and = (c, d)?
 Calculate the magnitude of the force with components of Fx = 12 N, Fy = 16 N, and Fz = 15 N. Calculate the magnitude of the force with components of Fx = 12 N, Fy = 16 N, and Fz = 15 N.
 What is the horizontal component of a force with a magnitude of 100 N that is directed 60° above the horizontal? What is the horizontal component of a force with a magnitude of 100 N that is directed 60° above the horizontal?
 Calculate the magnitude of a force given by Calculate the magnitude of a force given by
= (5, 12) N.
 What is the vertical component of a 64 N force directed 53° above the horizontal? What is the vertical component of a 64 N force directed 53° above the horizontal?
 Find the components of the resultant of the following forces: 15 N up, 8 N down, 4 N left, 20 N right. Find the components of the resultant of the following forces: 15 N up, 8 N down, 4 N left, 20 N right.
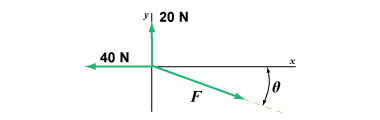
 Determine the force required to make the net force zero in the diagram above. Determine the force required to make the net force zero in the diagram above.
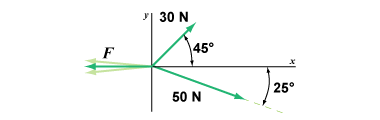
 Determine the force required to make the net force zero in the diagram above. Determine the force required to make the net force zero in the diagram above.
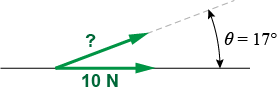
 What magnitude force at a 17° angle above the horizontal will produce a 10 N horizontal component force? What magnitude force at a 17° angle above the horizontal will produce a 10 N horizontal component force?
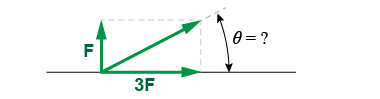
 At what angle should a force be applied so that its x-component is three times that of its y-component? At what angle should a force be applied so that its x-component is three times that of its y-component?
|

