Match each word to the sentence where it best fits.
| resultant vector | | resolution of forces | | cosine | | tangent | | sine | | component force | | magnitude | | component | |
- ________ is the ratio of the adjacent side over the hypotenuse.
- The process of breaking a force down into its components is called ___________.
- The _______ of a force vector is its strength in newtons.
- The _______ differs from the sine and cosine because it does not depend on the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
- The ________ is the single vector that is the sum of two or more vectors.
- The part of a force that lies on the x-axis is a ______
- _______ is most useful to solve for the vertical component of a force.
- For the vector (6,2) N, two newtons is the _______ in the y-direction.
| polar coordinates | | displacement | | velocity | | compass | | acceleration | | speed | | Cartesian coordinates | |
- A ship’s navigator would use a/an ________ to determine a direction when plotting a course.
- In the expression v0 cos θ, the variable v0 is the ________.
- The average _______ vector is the change in velocity divided by the change in time.
- A force that is described as 50 N at 30° is an example of a vector in ________.
- The average ___________ vector is calculated by dividing the displacement by the time.
- A change from one position vector to another is called a/an _________.
| | - A force that is 12 N in the x-direction and 6 N in the y-direction is an example of using _______ to describe the vector.
| projectile | | range | | trajectory | | ramp coordinates | | inclined plane | |
- A/An __________ is a moving body traveling only under the influence of gravity.
- An example of ________ would be the horizontal distance a soccer ball moves between being kicked and touching the ground again.
- Another term for ramp is _______.
- A kicked soccer ball follows a parabolic path called its _______.
- _______ is the rotated reference frame where the x-direction is along the surface of an inclined plane.
- Is it possible for a single 100 N force to have zero effect in the x-direction? If so, then describe how this might be possible.
- Is it possible for three forces to have a resultant of zero even if all three forces have different magnitudes? If so, then explain or sketch how this might be possible.
- What is the sin-1(sin30º)?
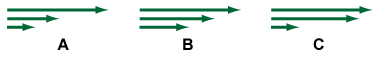
- Which of the three vector diagrams would best represent force of 2 N, 4 N, and 8 N?
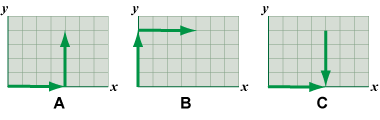
- Which of the three diagrams above does not correctly show the addition of the two vectors on a vector diagram.
 Describe how to transform a force that is in x–y components into a force of the same magnitude and opposite direction. Describe how to transform a force that is in x–y components into a force of the same magnitude and opposite direction.
|

