 In this chapter, you learned the last of the seven fundamental quantities in physics. Name all seven and provide the SI unit for each. In this chapter, you learned the last of the seven fundamental quantities in physics. Name all seven and provide the SI unit for each.
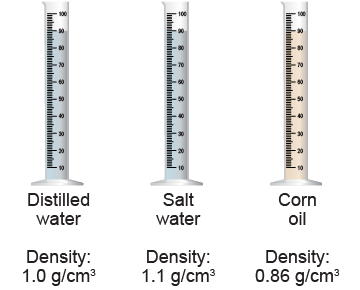
- The three graduated cylinders in the diagram above have the same depth of liquid. Which one has the highest pressure at the 20 mL mark? Explain your reasoning in one sentence.
 The units of pressure are newtons per meter squared and the units of volume are cubic meters. What are the units of pressure × volume? What other very important physical quantity has these units? The units of pressure are newtons per meter squared and the units of volume are cubic meters. What are the units of pressure × volume? What other very important physical quantity has these units?
- In the kinetic theory, what contributes to the internal energy of a solid other than the molecular kinetic energy of the individual particles?
- When you take in a deep breath, does the air inside your lungs have more ordered or random kinetic energy?
- Which equation would you use to calculate the thermal energy per atom for a gas?
-
-
-
 The air in Luigi’s classroom has a temperature of approximately 20°C, so he calculated vth = 502 m/s. What is the speed of the air molecules in his classroom? The air in Luigi’s classroom has a temperature of approximately 20°C, so he calculated vth = 502 m/s. What is the speed of the air molecules in his classroom?
 Which feels hotter, 100°F or 40°C? Which feels hotter, 100°F or 40°C?
| |  During the summer an air conditioner is set to cool the room air down to 76°F. What temperature does this correspond to in degrees Celsius? During the summer an air conditioner is set to cool the room air down to 76°F. What temperature does this correspond to in degrees Celsius?

 The heating boiler or furnace in your home has a label similar to the example shown here. Which of the numbers describes the heat output? What units are used? Express the heat output of your own furnace or boiler in watts. The heating boiler or furnace in your home has a label similar to the example shown here. Which of the numbers describes the heat output? What units are used? Express the heat output of your own furnace or boiler in watts.
 The hottest temperature ever recorded in the continental United States was 56.7°C. What does this correspond to in degrees Fahrenheit? The hottest temperature ever recorded in the continental United States was 56.7°C. What does this correspond to in degrees Fahrenheit?
 How much energy is required to raise the temperature of 200 g of water from 10°C to 20°C? (The specific heat of water is 4.18 J g−1 °C−1.) How much energy is required to raise the temperature of 200 g of water from 10°C to 20°C? (The specific heat of water is 4.18 J g−1 °C−1.)
 Your lab supervisor tells you to heat a chemical until it is 165ºF. What should your thermometer (which measures in degrees Celsius) read when it reaches the correct temperature? Your lab supervisor tells you to heat a chemical until it is 165ºF. What should your thermometer (which measures in degrees Celsius) read when it reaches the correct temperature?
 In order to use a certain equation, you need to plug in the absolute temperature (K). The temperature is 25ºC. What number should you use? In order to use a certain equation, you need to plug in the absolute temperature (K). The temperature is 25ºC. What number should you use?
 A mole is a furry animal with an average mass of 0.8 kg. How much mass would a mole of moles (the animal) have? A mole is a furry animal with an average mass of 0.8 kg. How much mass would a mole of moles (the animal) have?
 What is the mass of one krypton atom? (The atomic mass of krypton is 84 g.) What is the mass of one krypton atom? (The atomic mass of krypton is 84 g.)
 Rory eats a candy bar and then runs for a long time. He wonders how much energy he got from the candy bar to do all that running, so he looks at the label, which says “Serving Size 1 bar, Calories Per Serving: 260.” How many joules of food energy did the candy bar provide? Rory eats a candy bar and then runs for a long time. He wonders how much energy he got from the candy bar to do all that running, so he looks at the label, which says “Serving Size 1 bar, Calories Per Serving: 260.” How many joules of food energy did the candy bar provide?
 If you add 100 g of water at 80°C to 500 g of water at 20°C, and there is no heat loss to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the mixture of water? If you add 100 g of water at 80°C to 500 g of water at 20°C, and there is no heat loss to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the mixture of water?
 A 0.5 kg ball of an unknown metal absorbs 5,775 J of energy when it heats up from 20°C to 50°C. A 0.5 kg ball of an unknown metal absorbs 5,775 J of energy when it heats up from 20°C to 50°C.
- Calculate the specific heat capacity of the material.
- Look up the specific heat capacities of various metals. What metal is the ball made of?
|

