- What combination of lenses would you use to create a telescope similar to Kepler’s?
 What combination of lenses would you use to recreate Galileo’s telescope? What combination of lenses would you use to recreate Galileo’s telescope?
- Light enters a rhinestone at an angle of incidence of 40.0° and refracts to an angle of 23.4°. What is the index of refraction of the rhinestone?
 Light from air enters a diamond (n = 2.42) on a ring at an angle of 45°. What is the angle of refraction of the light when inside the diamond? Light from air enters a diamond (n = 2.42) on a ring at an angle of 45°. What is the angle of refraction of the light when inside the diamond?
 Light in a window (n = 1.52) hits the boundary with air at an angle of 55°. Will this light reflect off the boundary? Light in a window (n = 1.52) hits the boundary with air at an angle of 55°. Will this light reflect off the boundary?
 Imagine that at the end of Earth’s atmosphere there is a clear boundary between air (n = 1.0003) and the vacuum of space (n = 1). (This is not actually the case.) Imagine that at the end of Earth’s atmosphere there is a clear boundary between air (n = 1.0003) and the vacuum of space (n = 1). (This is not actually the case.)
- If sunlight enters the atmosphere from space at an angle of incidence of 30°, what is the angle of refraction?
- What is the critical angle for light leaving Earth’s atmosphere?
 A cube of ice (n = 1.31) sits in an unknown liquid. Light in the liquid hits the ice at an angle of 35.0° and refracts to an angle of 41.1°. What is the index of refraction of this liquid? A cube of ice (n = 1.31) sits in an unknown liquid. Light in the liquid hits the ice at an angle of 35.0° and refracts to an angle of 41.1°. What is the index of refraction of this liquid?
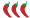 A ray of sunlight in the air (n = 1.00) hits a calm pool of water (n = 1.33) at an angle of 40.0° and is refracted as it passes the boundary. A ray of sunlight in the air (n = 1.00) hits a calm pool of water (n = 1.33) at an angle of 40.0° and is refracted as it passes the boundary.
- What is the angle of refraction after the ray has entered the water?
- Later, it is cold, and a layer of ice (n = 1.31) has formed on top of the water. If the ray enters the ice at the same angle, travels through the ice, and enters the water, what is its angle of refraction in the water?
- Create an algebraic relationship for a light ray that passes through three materials (n1, n2, n3) successively that relates the initial angle (θ1) to the final angle (θ3).
 Melinda places an object 50 cm in front of a thin convex lens with a focal length of 30 cm. What is the magnification of the image? Melinda places an object 50 cm in front of a thin convex lens with a focal length of 30 cm. What is the magnification of the image?
| | - Shireen has a magnifying glass and wants to use it to focus the Sun’s light onto a sheet of paper. When she holds the magnifying glass 6 cm away from an object, the object is magnified by 4. How close should she hold the paper to the magnifying glass to catch the focused sunlight?
 A 3-cm-wide stamp is held 4 cm in front of a magnifying glass that has a focal length of 12 cm. A 3-cm-wide stamp is held 4 cm in front of a magnifying glass that has a focal length of 12 cm.
- Where does the image appear?
- How large is the image of the stamp?
 An object is placed 40 cm away from a lens and an image is projected 120 cm away on the other side. What is the focal length of this lens? An object is placed 40 cm away from a lens and an image is projected 120 cm away on the other side. What is the focal length of this lens?
 Saul places an object 40 cm in front of a thin convex lens. The resulting image has a magnification of 2.5. What is the focal length of the lens? Saul places an object 40 cm in front of a thin convex lens. The resulting image has a magnification of 2.5. What is the focal length of the lens?
 Maria places an object 30 cm in front of a thin convex lens with a focal length of 50 cm. Maria places an object 30 cm in front of a thin convex lens with a focal length of 50 cm.
- What is the magnification of the image?
- Is the image inverted or upright?
- Is the image real or virtual?
 Vladamir wants to project a piece of artwork that is 0.5 m tall onto a screen that is 3.0 m tall. He has a convex lens with a focal length of 2.0 m. Vladamir wants to project a piece of artwork that is 0.5 m tall onto a screen that is 3.0 m tall. He has a convex lens with a focal length of 2.0 m.
- At what distance from the lens should he place his artwork to completely fill the screen?
- How far should the lens be from the screen?
- What orientation should his artwork have to produce an upright image?

 The two lenses shown are separated by 100 cm to form a compound optical device for an object placed 50 cm in front of the objective. The two lenses shown are separated by 100 cm to form a compound optical device for an object placed 50 cm in front of the objective.
- What is the image distance for the image formed by lens A?
- What is the magnification for lens A?
- Is this image real or virtual?
- Is this image upright or inverted?
- What is the object distance for lens B?
- What is the image distance for the image created by lens B?
- Is this image upright or inverted?
- Is this image real or virtual?
- Are these lenses properly set up to act as a telescope?
|

