- What piece of equipment would you use to measure an angle: a compass, a magnetic compass, a metric rule, a protractor, or a refractor?
 Light refracts from one material into another with some angle of incidence and angle of refraction. If you change the angle of incidence so that the sine of the angle doubles, what happens to the sine of the angle of refraction? Light refracts from one material into another with some angle of incidence and angle of refraction. If you change the angle of incidence so that the sine of the angle doubles, what happens to the sine of the angle of refraction?
 A ray of light enters a glass window at a certain angle of incidence and passes through. How will the angle of refraction compare when that ray of light exits the other side of the window? A ray of light enters a glass window at a certain angle of incidence and passes through. How will the angle of refraction compare when that ray of light exits the other side of the window?
 What is the range of possible values of the critical angle when light is passing into a material with a higher index of refraction (for example, from air to water)? What is the range of possible values of the critical angle when light is passing into a material with a higher index of refraction (for example, from air to water)?
 Typically, a mirror is a reflective surface covered in glass. Does the refraction of light through glass affect the angle at which light reflects? Explain. Typically, a mirror is a reflective surface covered in glass. Does the refraction of light through glass affect the angle at which light reflects? Explain.
 Ilana shines a ray of light through water into two mystery materials, A and B, with an angle of incidence of 30°. The angle of refraction for material A is 15°. The angle of refraction for material B is 20°. Ilana shines a ray of light through water into two mystery materials, A and B, with an angle of incidence of 30°. The angle of refraction for material A is 15°. The angle of refraction for material B is 20°.
- Does the ray bend more or less in material B than in material A?
- Which material has the higher index of refraction?
 Suppose a light ray shines through water, refracts into a thin straight layer of glass, and then refracts from the glass into air. Explain why the angle of refraction is the same into the air even if you remove the glass. (Hint: Write down Snell’s law for each time the ray refracts.) Suppose a light ray shines through water, refracts into a thin straight layer of glass, and then refracts from the glass into air. Explain why the angle of refraction is the same into the air even if you remove the glass. (Hint: Write down Snell’s law for each time the ray refracts.)
- Describe the procedure for ray tracing to locate the image formed by a convex lens.
- Kaleb has a lens, an object, and a screen. No matter where he puts the object, he can’t project it onto the screen. What kind of lens does he have?
- Claudius is looking through a lens in a door that allows him to see a very large field of view. Is his lens a diverging or converging lens?
- Name a common use for a convex lens.
| | - An object is placed in front of a thin, convex lens and its image has a negative magnification. What does this imply about the image?
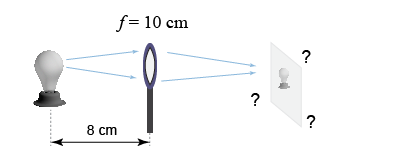
- A student has a magnifying lens with a focal length of 10 cm and holds it 8 cm from a light source. Will she be able to project an image of the light source onto a piece of paper?
 What material discussed in this chapter would make the most powerful lens, i.e., bend light the most? Why? What material discussed in this chapter would make the most powerful lens, i.e., bend light the most? Why?
 Linda wants to project an image onto a screen using a lens. Should she use a concave or convex lens? Linda wants to project an image onto a screen using a lens. Should she use a concave or convex lens?
 Where should an object be placed in relation to a convex lens to produce a virtual image? Where should an object be placed in relation to a convex lens to produce a virtual image?
 An object is placed several focal lengths away from a convex lens. Describe the resulting image. An object is placed several focal lengths away from a convex lens. Describe the resulting image.
 Use a piece of graph paper to draw the following and find the location and size of the image graphically. Draw a bi-convex lens and an optical axis passing through it. The convex lens has a focal length of 20 cm, so set a scale on your graph and draw both focal points. Place an object at an object distance of 30 cm from the lens and with a height of 5 cm. Draw light rays passing through the convex lens to locate the image. Use a piece of graph paper to draw the following and find the location and size of the image graphically. Draw a bi-convex lens and an optical axis passing through it. The convex lens has a focal length of 20 cm, so set a scale on your graph and draw both focal points. Place an object at an object distance of 30 cm from the lens and with a height of 5 cm. Draw light rays passing through the convex lens to locate the image.
- From your drawing, what is the image distance?
- From your drawing, what is the height of the image?
- Is the image inverted or upright?
- Is the image real or virtual?
- From your drawing, what is the magnification of the image?
- Which of the following compound optical devices usually has a prism inside?
- a refracting telescope
- a reflecting telescope
- Porro binoculars
- a compound microscope
- an SLR camera
- How do binoculars deliver an upright image of the object although refracting telescopes produce an inverted image?
|

