| | Essential questions | | What is the difference between real and virtual images?
How can you create real and virtual images with a convex lens? | |
|
Optical devices can create either real or virtual images. What’s the difference between the two? A real image is formed at a location where light rays actually converge, while a virtual image is formed at a location where light rays only appear to converge. In practical terms, a real image can be projected onto a piece of paper but a virtual image cannot. This morning you saw a virtual image of yourself in the mirror. Why was it virtual? Because you cannot put a sheet of paper behind the mirror and project your image onto it! A flat mirror produces a virtual image. How about a convex lens? 
|
Part 1: Create real and virtual images with a convex lens
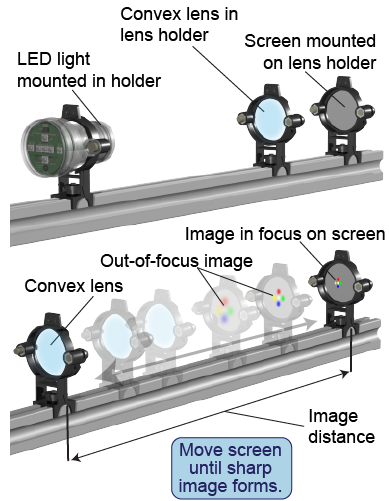 Caution: Never look directly at the LED light through the lens.
Caution: Never look directly at the LED light through the lens. - Mount the light source (the “object”) on the track near one end. Create the object by illuminating LEDs of different colors on the light source.
- Mount a convex lens at a distance of 60 cm from the LED light source. Mount the screen on the opposite side of the lens from the object.
- Adjust the screen location until you produce the sharpest possible image. Record whether the lens can produce a real image for this object distance.
- Move the lens closer to the object in steps of 5 cm and repeat the experiment, determining in each case whether a real image is formed.
- If you cannot project a focused image onto the screen no matter what distance, then what kind of image is being produced by the lens? Explain.
- At what object distances is the image real? At what distances is it virtual? How do you know?

|
Part 2: Image formation for other optical devices
- Leave the LED light source (the “object”) in place.
- Repeat the experiment with a convex lens, a concave mirror, and a convex mirror.
- For the mirrors, place a half screen in front of the lens (where the light rays are reflected!) so only half the mirror is covered. This allows you to look for the image without blocking all the light.
- With each of these three devices, determine whether it produces a real or a virtual image.
- Complete a table listing each optical device and the kind of image it produces. If it produces both real and virtual images, list the conditions under which it produces each kind of image.
- Which optical devices produce real images? Which produce virtual images? Which optical devices produce both real and virtual images?
- Under what conditions do these optical devices produce each kind of image?

|
| |
|

