|
How do binoculars, telescopes, microscopes, and cameras differ from a magnifying glass? A magnifying glass uses only one convex lens. Most optical instruments, however, use more than one optical element—lens, mirror, or disperser (e.g., prism)—and are called compound optics. 
|
Telescopes
|
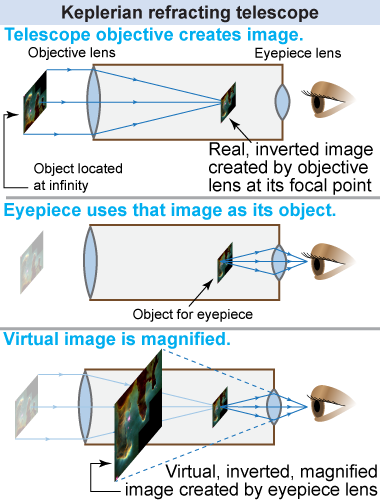
Galileo’s refracting telescope of 1609 used a convex objective lens (the lens at the entrance of the telescope) and a concave eyepiece lens (the lens in front of the observer’s eye). Within two years, the German mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler had invented a modified design that used two convex lenses. 
| 
|
In Kepler’s telescope, the objective lens takes the light from a distant object and forms an image at the focal point of the lens. This is not a very useful image by itself—try using a magnifying lens to look at something on the far wall! Instead, this image is used as the object for the eyepiece lens, which produces a magnified image. This then is the useful feature of a telescope: to magnify the image of a distant object, whether it is a far-away mountain peak or a galaxy. 
|
The largest refracting telescope today is 1 m in diameter, which is the maximum lens size that can be supported around its edge. Refracting telescopes also suffer from chromatic aberration: Light of different colors focuses at different points because the refractive index of glass varies with wavelength (as you will learn in Chapter 22). 
|
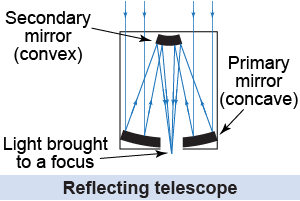 Isaac Newton built the first reflecting telescope to avoid the chromatic aberration problem in refractors. Modern telescopes also use curved mirrors instead of lenses because the large mirrors can be supported easily from the back. In a reflecting telescope, the light comes into the telescope and is redirected by a concave primary mirror. It then reflects off of a convex secondary mirror and is brought to a focus through a hole in the primary mirror.
Isaac Newton built the first reflecting telescope to avoid the chromatic aberration problem in refractors. Modern telescopes also use curved mirrors instead of lenses because the large mirrors can be supported easily from the back. In a reflecting telescope, the light comes into the telescope and is redirected by a concave primary mirror. It then reflects off of a convex secondary mirror and is brought to a focus through a hole in the primary mirror. 
 |
 Over the years, the diameter of telescopes has gotten larger and larger. Why? The primary reason why visible light telescopes are made larger is to increase their collecting area. The larger the aperture, the more light gets collected and the fainter are the astronomical sources that can be detected. The 10.4 m diameter Keck telescopes on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, can take images and spectra of faint galaxies at the edge of the visible universe!
Over the years, the diameter of telescopes has gotten larger and larger. Why? The primary reason why visible light telescopes are made larger is to increase their collecting area. The larger the aperture, the more light gets collected and the fainter are the astronomical sources that can be detected. The 10.4 m diameter Keck telescopes on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, can take images and spectra of faint galaxies at the edge of the visible universe!
An additional advantage for a larger-diameter telescope is that it improves the resolution of the images. For visible and infrared telescopes on the ground, Earth’s atmosphere blurs the image quality so that there is usually little gain in resolution. For telescopes in space, however, there is no atmosphere, so the images are not blurred. The Hubble Space Telescope takes images with very high resolution, such as the image of the “Whirlpool Galaxy” on the right! 
|
 There are many other kinds of telescopes, such as the Very Large Array of radio telescopes in Socorro, New Mexico. Each of these radio telescopes reflects radio waves—light with very long wavelengths—off a primary and a secondary mirror onto the scientific instruments. A radio telescope is a reflecting telescope!
There are many other kinds of telescopes, such as the Very Large Array of radio telescopes in Socorro, New Mexico. Each of these radio telescopes reflects radio waves—light with very long wavelengths—off a primary and a secondary mirror onto the scientific instruments. A radio telescope is a reflecting telescope! 
 |
 X-ray telescopes, such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory, use grazing incidence mirrors. The x-ray light strikes these mirrors at very high angles of incidence, such as 87° or 88°. At these high angles, x-ray light reflects off of the mirror surface instead of being absorbed by it. By using multiple mirror surfaces, all the x-rays from an astronomical source can be focused to a point on the detector. By using nested mirrors, the telescope increases its collecting area and can detect fainter sources.
X-ray telescopes, such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory, use grazing incidence mirrors. The x-ray light strikes these mirrors at very high angles of incidence, such as 87° or 88°. At these high angles, x-ray light reflects off of the mirror surface instead of being absorbed by it. By using multiple mirror surfaces, all the x-rays from an astronomical source can be focused to a point on the detector. By using nested mirrors, the telescope increases its collecting area and can detect fainter sources. 
|
What is the benefit of using mirrors instead of lenses in compound optics?
 |
- Lenses exhibit chromatic aberration, in which the different colors of light come to a focus at different locations. As a result, images spanning a range of wavelengths are blurred.
- Mirrors are easier to support. The supporting structure can be attached from the back. Lenses can only be supported from the edge, as light must be able to pass through the middle section. This means larger mirrors can be used compared with lenses, as heavier ones can be better supported.

|

