| | Essential questions | | How does light refract at a boundary?
What is the index of refraction of water? | |
|
Refraction may change the direction of light rays passing from one medium to another. The differences in index of refraction between the two media determine how much refraction occurs. In this investigation, you will analyze light rays passing through air and water and determine the index of refraction of water. 
|
Part 1: Trace the path of light through air and water
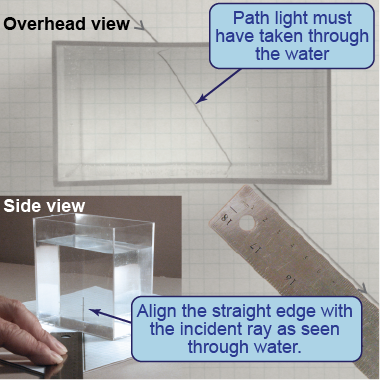
- Place the container in the middle of a piece of graph paper and trace its outline. Remove the container.
- Use a straight edge to draw an incident ray that intersects the left side of the container outline at an incident angle of about 45° to 50°.
- Fill the container with water and replace it.
- On the far side of the container, look through the water to view the incident ray. Align a straight edge with the incident ray as seen through the water. Use the straight edge to draw the refracted ray.
- Empty and replace the container. Align a straight edge with the incident ray as seen through the empty container. Draw and label the “refracted” ray.
- Remove the container. Connect the path of the light rays through both the full and empty containers.
- Did the light bend through the empty container? Through the water? Why or why not?
- When the light bent, in how many places did it bend?
- Construct the normals for both boundaries using dashed lines. With a protractor, measure and record the angles of incidence and refraction.
- Use the Snell’s law calculator to calculate the index of refraction of water for each boundary.

Part 2: Investigate the effect of angle on refraction
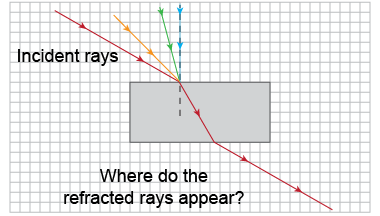
- Construct three more incident rays at angles smaller than 45°, including one ray with an angle of incidence of 0°.
- Refill and replace the container of water.
- Look through the container to view the incident rays. Draw the refracted rays with a straight edge.
- Remove the container and connect the path of the light rays. Then replace the container and view the complete set of rays.
- Did all rays through the water refract? Which rays refract the most? The least?
- What two factors have you found to determine how much a light ray will bend?
- Reverse position and look through the water to view the refracted rays. What do you notice? Why?

|
Snell's law of refraction in equation (21.1) is the relationship between the angle of incidence, angle of refraction, and index of refraction. Use this calculator to calculate the index of refraction of water using your measurements of the angles of incidence and refraction.
| | |
| |
|

