|
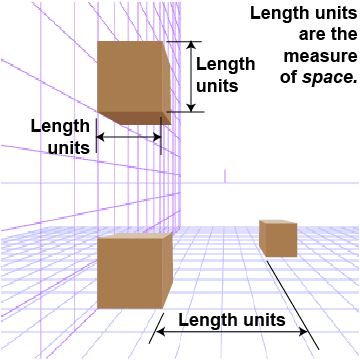 Think about space as a quantity of its own, independent of any matter that might be present. For example, how big is the space inside your classroom. How do you describe precisely where objects are located within the room? The answers to both questions involve the quantity of length. Length is the measure of space between two points. Like mass, length is a fundamental quantity: length is the dimension of space itself. Objects, such as rocks or people, take up space and therefore size is described with length units such as meters, feet, and inches.
Think about space as a quantity of its own, independent of any matter that might be present. For example, how big is the space inside your classroom. How do you describe precisely where objects are located within the room? The answers to both questions involve the quantity of length. Length is the measure of space between two points. Like mass, length is a fundamental quantity: length is the dimension of space itself. Objects, such as rocks or people, take up space and therefore size is described with length units such as meters, feet, and inches. 
|
There are thousands of different languages spoken among the seven billion people in the world. The concept of length is described in each one, often with a completely different word. As with languages, there are different units for describing the same length. For example, 1 meter, 39.37 inches, 3.28 feet, and 100 centimeters all describe the same length. There are two common systems of length units you need to know and understand. The English system uses inches (in), feet (ft), yards (yd), and miles (mi). The metric system uses millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), and kilometers (km). The light year is the distance light travels in one year—a very large distance!—and is suitable for measuring the distances between stars. 
|

|
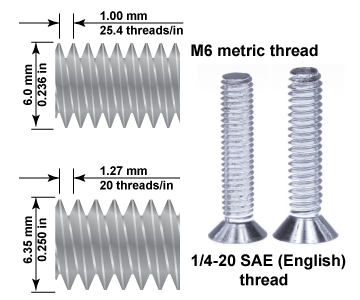 Screw threads provide an example of different length units. Nuts, bolts, and screws come in both English and metric threads that look similar but are not interchangeable. An M6 bolt has a diameter of 6 mm and each thread is 1 mm apart. A 1/4-20 bolt has a diameter of 1/4 inch and 20 threads per inch. A 1/4-20 screw will not thread into an M6 nut and vice versa. Because parts are made worldwide, and countries other than the USA use metric fasteners, American cars have a mixture of English and metric fasteners.
Screw threads provide an example of different length units. Nuts, bolts, and screws come in both English and metric threads that look similar but are not interchangeable. An M6 bolt has a diameter of 6 mm and each thread is 1 mm apart. A 1/4-20 bolt has a diameter of 1/4 inch and 20 threads per inch. A 1/4-20 screw will not thread into an M6 nut and vice versa. Because parts are made worldwide, and countries other than the USA use metric fasteners, American cars have a mixture of English and metric fasteners. 
|
Which unit of length is best for measuring each of the following? Choose from nanometer, micrometer, millimeter, meter, kilometer, astronomical unit, and light year. - length of a swimming pool
- distance from the Sun to Jupiter
- width of a coin
- diameter of the universe
- length of a mile
 |
- Meters; swimming pools will range in size from several meters to 50 m.
- Astronomical units; the average distance between Jupiter and the Sun is 5 AU.
- Millimeters; the width of coins is close to a millimeter. Dimes are 1.35 mm wide and quarters are 1.75 mm wide.
- Light years; there are billions of trillions of stars in the ever-expanding universe. The observable universe is billions of light years wide and may extend to infinity outside of that area.
- Kilometers; a mile is longer than a kilometer. Both are useful for measuring distances on the surface of Earth. A mile is 1.61 kilometers.

|
| |
|

