|
| Essential questions | | What are the magnifications of convex and concave mirrors?
Where are the images located for each? | |
|
Flat mirrors produce images that are the same size as the object and located an equal distance behind the mirror. What is the magnification for a curved mirror surface? Where are its images located? In this investigation, you will use an interactive simulation to study the properties of image formation for curved mirrors. You will then use the mirrors in the equipment kit to check the conclusions you drew from the simulations. 
|
Part 1: Image location and magnification for a convex mirror
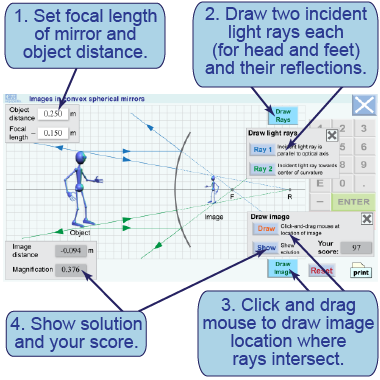
- Set the convex mirror’s focal length to 20 cm and the object distance to 30 cm.
- Press the buttons to show how the two incident light rays reflect from the mirror’s surface.
- Press the [Draw image] button and then click and drag the mouse at the location of the image.
- Show the solution and record your score. Tabulate the object distance, image magnification, image orientation (upright or inverted), and image location (in front of or behind the mirror).
- Repeat for object distances of 10 and 50 cm.
- Describe how you found the image location.
- Based on the simulation, what kinds of images does a convex mirror create?
- Pick up a real convex mirror and look at your image from different object distances. Do your simulation results agree with what you see?

|
|
This interactive element simulates forming images with a convex mirror. Set the focal length of the mirror and the object distance for the robot, then see how the light rays reflect off the mirror. The reflected light rays from the robot’s head intersect at the location of the image of its head. Draw the robot’s image where the light rays intersect and compare your answer with the correct answer.
|
Part 2: Image location and magnification for a concave mirror
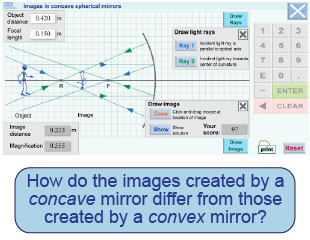
- Set the concave mirror’s focal length to 20 cm and the object distance to 50 cm.
- Repeat the procedure from Part 1, identifying the location of the image formed by the concave mirror.
- Repeat for object distances of 10 and 30 cm. Tabulate the results as before.
- Based on the simulation, what kinds of images does a concave mirror create? Under what conditions?
- How do the images created by a concave mirror differ from those created by a convex mirror?
- Pick up a real concave mirror and look at your image from different object distances. Do your simulation results agree with what you see?

|
This interactive element simulates forming images with a concave mirror. Set the focal length of the mirror and the object distance for the robot, then see how the light rays reflect off the mirror. The light rays from the robot’s head intersect at the location of the image of its head. Draw the robot’s image where the light rays intersect and compare your answer with the correct answer.
| |

