|
Spherical mirrors can produce images that are larger or smaller than life size and right-side up or upside-down. These mirrors can be converging (concave) or diverging (convex). The center of curvature is the center of the sphere that defines the mirror’s reflecting surface. The optical axis is the path of a ray traveling through the center of an optical system. The optical axis of a spherical mirror is a line perpendicular to the mirror surface that passes through the center of curvature of the mirror. The focal point of a spherical mirror is the point through which rays parallel to the optical axis are reflected. The focal length of a spherical mirror is equal to half the radius of curvature. 
|
|
convex, concave, optical axis, focal point, focal length
|
Review problems and questions |
|
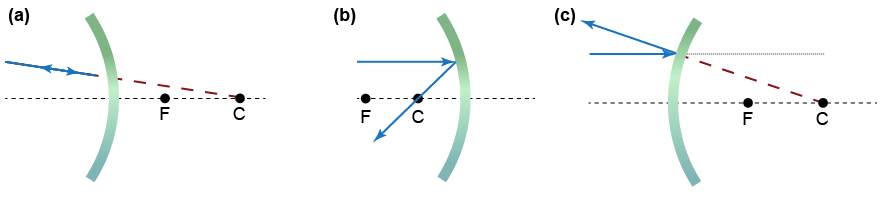
- A student drew the ray diagrams (above) to describe the reflection of light from different spherical mirrors. Each drawing has an error in it. For each illustration (a–c), describe what the student did wrong in drawing and/or labeling each ray diagram.


|
- The focal point F and center of curvature C should be drawn to the left of the concave mirror. After making this change, the path of a light ray that passes through the center of curvature will also change.
- The locations of the focal point and center of curvature have been switched; the center of curvature should be located further from the mirror than the focal point. Once that change is made, the reflected ray will be correctly drawn as passing through the focal point.
- For the drawn incident ray parallel to the optical axis, the reflected ray should reflect along a line passing through the focal point, not the center of curvature.

|
- Which of the following statements is not correct for drawing a ray diagram for a spherical mirror?
- Incident rays parallel to the optical axis reflect along a line passing through the focal point.
- The image is drawn where the two incident rays intersect.
- You can draw as many incident rays as you want in drawing a ray diagram.
- The image formed by a convex mirror is located behind the mirror.


|
Statement b is incorrect. A correct statement should read, “The image is drawn where the two reflected rays intersect.” 
|
- Which of the following statements is not correct for drawing a ray diagram for a spherical concave mirror?
- The object arrow can be placed at the center of curvature.
- The object arrow can be placed at the focal point.
- The image is always located between the center of curvature and the mirror surface.
- The object and the image arrows can be located at the same distance from the mirror.


|
Statement c is not correct. For a concave mirror, as you learned in the investigation, the image can be located either in front of or behind the mirror, depending on the object location. 
|
Take a Quiz |

