|
Light travels in straight lines in a vacuum but light rays may bounce (reflect) or bend (refract) upon interacting with matter. Many technologies and objects exhibit the reflection and/or refraction of light, including eyeglasses and contact lenses, mirrors in dressing rooms, rear-view mirrors on cars, a glass of water, and even the cut and polished diamond in a ring. The science and technology of manipulating light is the field of optics. 
|
Examples of optical devices
|
|
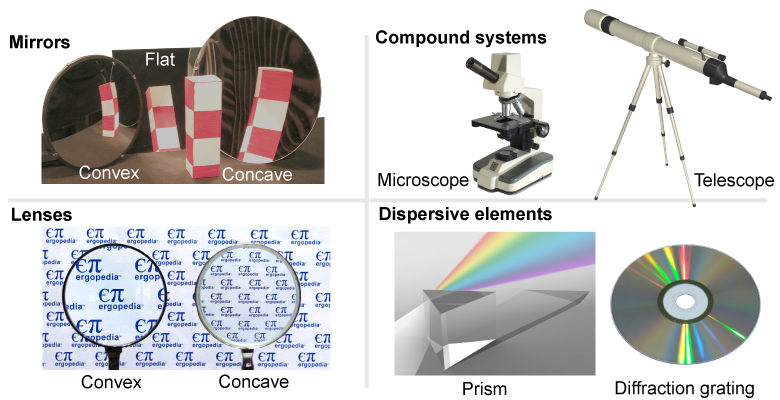
A mirror is a basic optical device that diverts light using reflection. Most large mirrors are flat, such as the mirror above the sink in a bathroom. Mirrors can also have curved surfaces, which create unusual reflections—especially the wavy mirrors found in a funhouse that make you look skinny or short! Most mirrors are made from clear glass with a thin layer of aluminum or silver sprayed on the back side to reflect light. Many metals can also be polished smooth and shiny to act as a mirror. 
 |
 The manufacturing process by which a metal is heated and then sprayed in a thin coating on one side of a piece of glass is called silvering. Centuries ago, mirrors were created simply by polishing a piece of metal, such as bronze, copper, or silver. But people soon realized that a clearer picture could be created by using glass in front of the metal surface—and that the metal, when heated to the liquid stage, could be deposited in a thin layer on one side of the glass to create the reflective surface. Most mirrors today use aluminum or silver as the metal coating. The coated surface is usually placed at the back side of the mirror, because the glass then protects the shiny metal surface from damage. An exception is the aluminum coating on the mirrors in telescopes: the coating is on the front-side of the glass, which is the surface that is precisely ground to a special shape to focus the incident light.
The manufacturing process by which a metal is heated and then sprayed in a thin coating on one side of a piece of glass is called silvering. Centuries ago, mirrors were created simply by polishing a piece of metal, such as bronze, copper, or silver. But people soon realized that a clearer picture could be created by using glass in front of the metal surface—and that the metal, when heated to the liquid stage, could be deposited in a thin layer on one side of the glass to create the reflective surface. Most mirrors today use aluminum or silver as the metal coating. The coated surface is usually placed at the back side of the mirror, because the glass then protects the shiny metal surface from damage. An exception is the aluminum coating on the mirrors in telescopes: the coating is on the front-side of the glass, which is the surface that is precisely ground to a special shape to focus the incident light.
Above right is an image of a coated telescope mirror for the James Webb Space Telescope. Instead of glass it uses beryllium, a material that deforms less than glass in the low temperatures of space. 
|
 A lens has a curved surface that bends light by refraction. Lenses are found in many optical technologies including magnifying glasses, microscopes, and all types of cameras including video cameras and the camera on the back of a mobile phone. Lenses are usually made from transparent polished glass or plastic.
A lens has a curved surface that bends light by refraction. Lenses are found in many optical technologies including magnifying glasses, microscopes, and all types of cameras including video cameras and the camera on the back of a mobile phone. Lenses are usually made from transparent polished glass or plastic. 
|
A prism is an optical device with flat surfaces that uses refraction to divert the path of light. Because different colors of light refract at slightly different angles, a prism may disperse white light into its constituent colors. Dispersion explains how a triangular prism separates a beam of white light into the colors of the rainbow. Prisms in technology are made from transparent polished glass or plastic. In nature, droplets of water act as tiny prisms to create rainbows. 
|
| |
|

