| | Essential questions | | How is resistance measured? | |
|
Ohm’s law, I = V/R, is the fundamental relationship among current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. Devices that measure resistance are based on Ohm’s law. These devices apply a known voltage and/or current, then determine the resistance. In this investigation you will use a similar experimental technique to measure the resistance of a lamp. 
|
Part 1: Current through different resistors
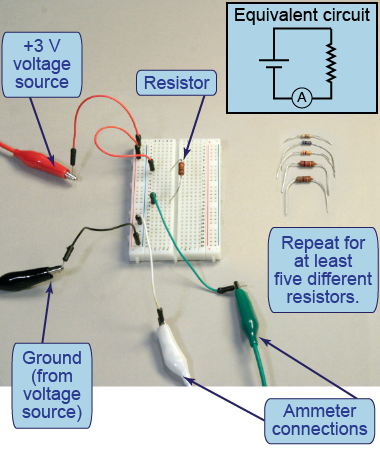
- Find a 100 Ω resistor. You will have to read the resistor values using their colored bands.
- Construct the circuit on the breadboard, and power it using a +3 V power supply (or two D-cell batteries).
- Connect an ammeter in series with the resistor and measure the current through the resistor.
- Repeat the experiment for at least four other resistors between 50 Ω and 2 kΩ (2,000 Ω). Tabulate your results for R and I. Calculate 1/R in each case.
- Graph I on the vertical axis and R on the horizontal axis.
- Make a second graph with I on the vertical axis and 1/R on the horizontal axis and measure the slope of the graph.
- Describe the relationship between current and resistance for a fixed voltage.
- What is the value of the slope of your second graph?
- What does the slope of this graph represent? Why?

How to do Part 1 using a myDAQ
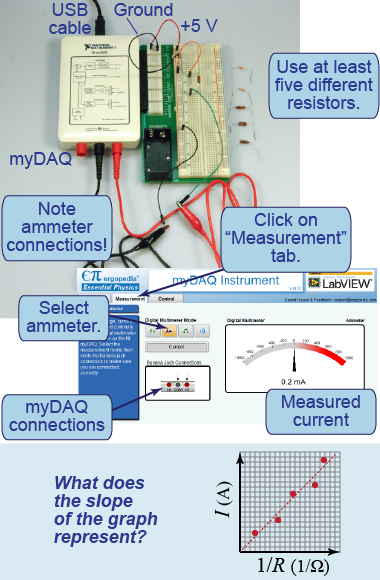 You can conduct a similar investigation using the myDAQ. In this case, you will use a fixed voltage of +5 V, vary the resistance (using resistors from 50 Ω to 2 kΩ), and measure the current for each case.
You can conduct a similar investigation using the myDAQ. In this case, you will use a fixed voltage of +5 V, vary the resistance (using resistors from 50 Ω to 2 kΩ), and measure the current for each case.
- Gather a supply of resistors with rated values from 50 Ω to 2 kΩ. You will have to read the resistor values using their colored bands.
- Construct the circuit on the breadboard using a single resistor, and power it using the myDAQ power supply set to 5 V.
- Measure the current through the resistor.
- Repeat the experiment for at least four additional resistors. Tabulate your results.
- Graph your data with I on the vertical axis and R on the horizontal axis.
- Create a second graph with I on the vertical axis and 1/R on the horizontal axis. Fit a straight line to your data and measure the slope of the line.
- Describe the relationship between current and resistance for a fixed voltage.
- What is the value of the slope of your second graph?
- What does the slope of this graph represent? Why?
Part 2: Resistance of a light bulb
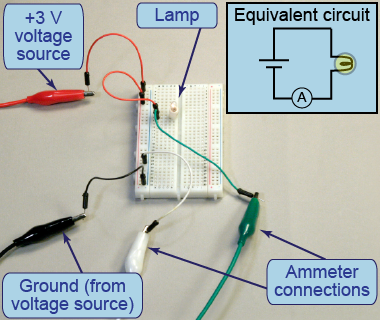
- Replace the resistor with the lamp.
- Measure the current through the illuminated lamp.
- Calculate the resistance of the lamp using Ohm’s law, Rmeas = V/I.
- What is the resistance of the lamp?
- Imagine you have a complicated circuit containing many resistors. Describe in words how you can use Ohm’s law to find the effective resistance of the entire circuit.

|
How to do Part 2 using a myDAQ
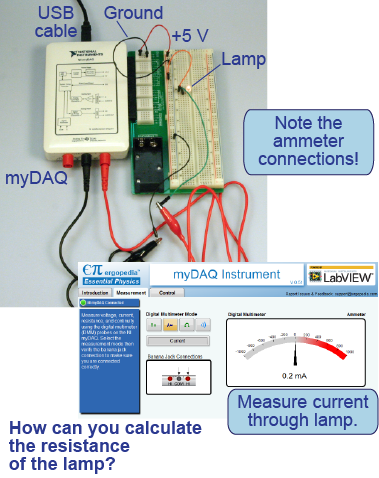 You can use the myDAQ to measure the current through the lamp and thus calculate the resistance through the lamp.
You can use the myDAQ to measure the current through the lamp and thus calculate the resistance through the lamp.
| | |
| |
|

