|
Compare the two circuits below. The voltage is the same, but the two-bulb circuit draws more total current. How do you determine the total current in the circuit? To help answer the question, consider that current flows out of the battery according to Ohm’s law: The current is the battery voltage divided by the total resistance of the circuit. What resistance does the battery “see” from its terminals? 
|
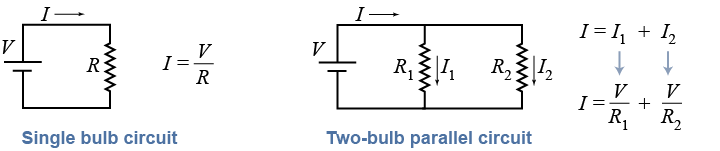
|
According to Ohm’s law, the current in each branch of the circuit is the battery voltage V divided by the resistance of that branch (R1 or R2). Next, note that the current flowing out of the battery is the sum of the currents in the two branches (from Kirchhoff’s current law). 
|
 If you compare this with Ohm’s law, the inverse of the total resistance as seen by the battery is equal to the sum of the inverses of the individual branch resistances. This leads directly to equation (17.4), which gives the total resistance R for a parallel circuit containing three individual resistances:
If you compare this with Ohm’s law, the inverse of the total resistance as seen by the battery is equal to the sum of the inverses of the individual branch resistances. This leads directly to equation (17.4), which gives the total resistance R for a parallel circuit containing three individual resistances: 
|
| (17.4) | | | R | = | equivalent resistance (Ω) | | R1 | = | resistance 1 (Ω) | | R2 | = | resistance 2 (Ω) | | R3 | = | resistance 3 (Ω) |
| Equivalent resistance
parallel resistors |
|
Adding more branches to a parallel circuit always increases the total current in the circuit. From the perspective of the battery, the total resistance of the circuit must decrease, because more total current flows while the voltage stays the same. Equation (17.4) reflects this behavior mathematically. 
|
What is the equivalent resistance of two 10 Ω resistors connected in parallel? | Asked: | equivalent resistance Req | | Given: | individual resistances R1 = 10 Ω and R2 = 10 Ω | | Relationships: | | |
| | Solution: | Add the resistances by finding a common denominator: | |
If (1/Req) = 1/(5 Ω), then Req = 5 Ω. | | Answer: | Req = 5 Ω. | 
|
If you connect three identical resistors in series and in parallel, in which case will they have a smaller equivalent resistance?
 |
The resistors connected in parallel will have a smaller total resistance. The series resistors will have a total circuit resistance of 3R, whereas the parallel resistors will have a total circuit resistance of R/3. In a parallel circuit, the total circuit resistance will always be less than any of the individual resistances. In a series circuit, the total circuit resistance will always be greater than each of the individual resistors. 
|

