|
Energy is a topic of concern to us all. We increasing desire a secure, affordable, and unlimited energy supply, but the environmental side effects of fossil fuels and nuclear power have become major concerns. Renewable energy may be the key to meeting our energy needs in an ecologically sustainable way. What do we mean by renewable energy? Is any “natural” form of energy renewable? The answer is no. Nature created the fossil fuels that we burn to supply most of our energy needs today, but it took millions of years to build up these reserves of coal, oil, and natural gas that civilization will deplete in only one or two centuries. Renewable energy includes forms of energy that we do not destroy, deplete, or disrupt faster than nature can restore or replenish them. 
|
 Solar energy derives power from the radiant energy in sunlight. Sunlight can be used to heat water for household use; it can be used to create steam, which then powers a turbine; and it can directly generate electric current when absorbed by a photovoltaic cell.
Solar energy derives power from the radiant energy in sunlight. Sunlight can be used to heat water for household use; it can be used to create steam, which then powers a turbine; and it can directly generate electric current when absorbed by a photovoltaic cell. 
|
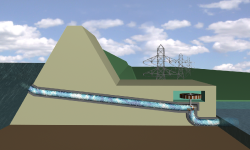 Hydroelectric energy refers to the mechanical energy of water flowing from higher places to lower ones. For centuries, this energy has crushed grain and spun lathes in mills built alongside rivers and waterfalls; today it is used mainly to generate electricity.
Hydroelectric energy refers to the mechanical energy of water flowing from higher places to lower ones. For centuries, this energy has crushed grain and spun lathes in mills built alongside rivers and waterfalls; today it is used mainly to generate electricity. 
 |
The chemical energy in gasoline contains 35 MJ (million joules) of energy in each liter; a car on the highway may use 10 L of gasoline per hour, corresponding to an average input power of 97 kilowatts (kW).
The gravitational potential energy of water at the top of the Hoover Dam is far less per liter—around 1.8 kJ (1,800 J)—but the Colorado River delivers so much water (averaging 500,000 L/s!) that the entire dam runs at an average power of nearly 500 million watts (MW).
The average radiation of the Sun (accounting for clouds and nighttime conditions) is around 200 W/m2, so a photovoltaic cell installation on a house’s 100 m2 rooftop can produce 3 kW of power (assuming 15% of the sunlight is converted to electrical power), or enough to power one-half to three-fourths of a typical household’s electricity needs.
Chemical energy such as that in gasoline has high energy content but limited quantities are available, while solar and hydro power sources have low energy content but vast potential quantities. 
|
 Wind energy has long been used to pump water or grind grain. Wind energy is today increasingly being tapped to generate electricity. Ultimately, wind derives its power from sunlight and, to a lesser extent, from Earth’s rotation.
Wind energy has long been used to pump water or grind grain. Wind energy is today increasingly being tapped to generate electricity. Ultimately, wind derives its power from sunlight and, to a lesser extent, from Earth’s rotation. 
|
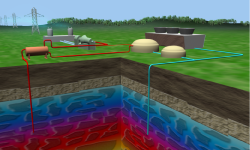 Geothermal energy is thermal energy and pressure contained within underground bodies of water heated by magma—molten rock that rises from deep within the Earth. Hot springs and geysers are two natural geothermal phenomena.
Geothermal energy is thermal energy and pressure contained within underground bodies of water heated by magma—molten rock that rises from deep within the Earth. Hot springs and geysers are two natural geothermal phenomena. 
|
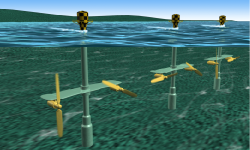 Tidal energy ultimately comes from the gravitational interaction among the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. This interaction causes ocean water to flow back and forth twice daily. Tides involve tremendous amounts of mechanical energy—energy that is hardly tapped today.
Tidal energy ultimately comes from the gravitational interaction among the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. This interaction causes ocean water to flow back and forth twice daily. Tides involve tremendous amounts of mechanical energy—energy that is hardly tapped today. 
|
 Nuclear fusion derives energy through nuclear reactions that combine lighter elements into heavier elements. Nuclear fusion is the energy source for the Sun and stars. A practical fusion reactor, however, has yet to be developed. (The opposite process, nuclear fission, powers today’s nuclear plants.)
Nuclear fusion derives energy through nuclear reactions that combine lighter elements into heavier elements. Nuclear fusion is the energy source for the Sun and stars. A practical fusion reactor, however, has yet to be developed. (The opposite process, nuclear fission, powers today’s nuclear plants.) 
 |
Nuclear fusion is not truly renewable—it consumes deuterium taken from seawater. But it could power our lifestyle for millions of years, as fusion is extremely efficient. Nuclear fusion powers the Sun and hydrogen bombs. Albert Einstein’s famous formula, E = mc2, specifies the amount of energy that can be obtained from a given amount of mass. Since the speed of light c is so great, a very small amount of mass m can generate a significant amount of energy. 
|
Which of the above-listed forms of renewable energy is fundamentally a form of mechanical energy? (There may be more than one right answer.)
 |
Hydroelectric energy, wind energy, and tidal energy all are based on the mechanical energy of a fluid (water in two cases and air in the third)—they all rely on the fact that the fluid is moving or has the potential to do so because of its position (elevation). By contrast, solar power exploits the energy contained in a form of electromagnetic radiation (sunlight), while geothermal power makes use of steam pressure and the thermal energy contained in water, rocks, and soil. 
|

