|
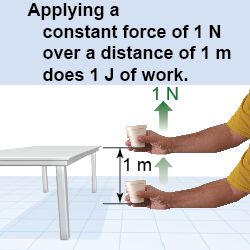 How does energy move and create change? The answer starts with the physical idea of work. In physics, work is done by forces that cause objects to move. As shown in equation (9.1), the amount of work done on an object is the force multiplied by the distance the object moves in the direction of the force. If you use a force of one newton to lift a cup up a distance of one meter, you do one newton-meter (N m) of work on the cup.
How does energy move and create change? The answer starts with the physical idea of work. In physics, work is done by forces that cause objects to move. As shown in equation (9.1), the amount of work done on an object is the force multiplied by the distance the object moves in the direction of the force. If you use a force of one newton to lift a cup up a distance of one meter, you do one newton-meter (N m) of work on the cup. 
 |
In physics, you can exert a force, even a large force, and yet do no work if nothing moves. Pushing against a brick wall does no work on the wall as long as the wall does not move. This part of the definition of work is less intuitive, because your body does work on itself when your muscles move. However, no work is done on the wall, because the wall does not move. All the work done by your muscles is converted to heat and chemical energy in the form of lactic acid and other metabolites. 

|
| (9.1) | | | W | = | work (J) | | F | = | force (N) | | d | = | distance (m) |
| Work
|
|
The meaning of the word “work” is different in physics from how we use the word in everyday life. You might complain that you work too hard on your homework or that you have to go to work early in the morning. In physics, work is the product of force exerted and distance moved, and it can have a precise value such as 10 N m. Work is done whenever energy is transferred from one object to another. 
|
|
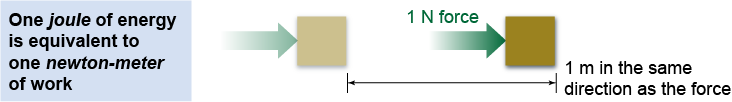
In the SI system, one joule (J) is defined as one newton-meter (N m). The unit of work—the joule—is also the basic unit of energy. Throughout physics and throughout all of science—including chemistry, biology, and earth sciences—you will find the joule as a standard unit of energy. It is not, however, the only unit of energy. Calories (food), British thermal units (heat), and kilowatt-hours (electricity) are other units of energy that are commonly used. 
|
|
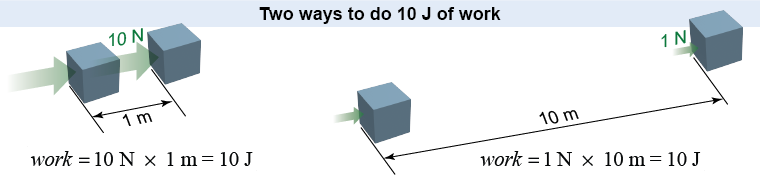
Work provides an operational definition for energy: Energy is the ability to do work. If you have 10 J of energy, you have the ability to produce a force of 10 N for a distance of 1 m, or 1 N for 10 m. A system that has 1 J of energy can exert any combination of forces and distances whose product is equal to or less than 1 N m. We say “less than” because the amount of energy available limits the amount of work that can be done. No system can produce any work that exceeds its available energy. 
 |
Although defining energy in terms of work is based on the mechanical idea of forces and movements, it is a surprisingly versatile definition that accurately extends into electrical energy, thermal energy, and even light energy. A great many human technological inventions are fundamentally devices for turning energy of other forms into work. For example, the electric motor turns electrical energy into work. It is only when we get into the quantum world inside the atom that we need to broaden the definition of energy. In the quantum world the concepts of force and distance become somewhat fuzzy and indefinite. Although energy exists inside of atoms, its description in terms of mechanical work becomes inadequate. 

|
Tim pulls his little sister in a wagon with a constant force of 50 N over a distance of 100 m. How much work does Tim do? - 5,000 J
- 2,500 J
- 150 J
- 50 J
 |
Asked: work W done on cart
Given: Tim exerts force F = 50 N; force is exerted over distance d = 100 m.
Relationships: W = Fd
Solve:
Answer: 5,000 J 
|

