|
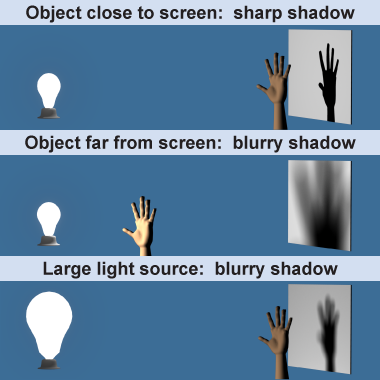 A shadow is direct evidence that light travels in straight lines. If light were to curve around objects, then shadows would not form as they do. The sharpness of a shadow is determined both by the size of the light source and the relative separation between the light source, object, and the surface (screen) on which the shadow appears. Dispersed light sources, such as overhead fluorescent tubes, create blurry shadows. If an object is close to a light source, then the edges of its shadow also become blurred.
A shadow is direct evidence that light travels in straight lines. If light were to curve around objects, then shadows would not form as they do. The sharpness of a shadow is determined both by the size of the light source and the relative separation between the light source, object, and the surface (screen) on which the shadow appears. Dispersed light sources, such as overhead fluorescent tubes, create blurry shadows. If an object is close to a light source, then the edges of its shadow also become blurred. 
|
The straight line paths followed by light are shown in diagrams in the form of light rays. Light rays use arrows to show the direction in which the light travels. Think of a light ray is an idealized, infinitely narrow beam of light, like a laser beam. 
|
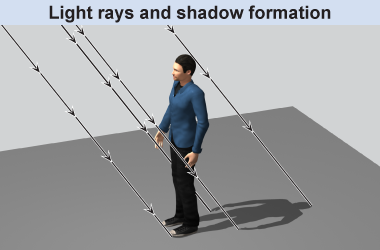 How a shadow forms is explained with a light ray diagram. Areas are illuminated where light rays can freely travel to the ground. Areas are shadowed where light rays are blocked. Although every point on an illuminated surface receives light, a ray diagram typically includes only a few of those light rays that best illustrate what we are trying to explain. For a shadow, the important rays are those that just graze the outline of the object casting the shadow.
How a shadow forms is explained with a light ray diagram. Areas are illuminated where light rays can freely travel to the ground. Areas are shadowed where light rays are blocked. Although every point on an illuminated surface receives light, a ray diagram typically includes only a few of those light rays that best illustrate what we are trying to explain. For a shadow, the important rays are those that just graze the outline of the object casting the shadow. 
|
This representation of light is called the ray model and it is useful for describing shadows, reflection, and refraction. Other models of light, such as the wave model and the photon model, are better for explaining other phenomena. The wave model describes polarization, interference, and diffraction. The photon model describes how light interacts with atoms. 
|
 Light from the Sun can only illuminate areas of Earth with a direct line of sight to the Sun. At any moment all areas of Earth facing the Sun are in daylight. Areas facing away from the Sun are in shadow and experience night. In essence, night is caused by Earth’s own shadow! The 24-hour cycle of day and night occurs because Earth’s 24-hour rotation continually changes the part of the planet facing the Sun.
Light from the Sun can only illuminate areas of Earth with a direct line of sight to the Sun. At any moment all areas of Earth facing the Sun are in daylight. Areas facing away from the Sun are in shadow and experience night. In essence, night is caused by Earth’s own shadow! The 24-hour cycle of day and night occurs because Earth’s 24-hour rotation continually changes the part of the planet facing the Sun. 
|
Which of the following does the ray model of light explain? - the photoelectric effect
- shadow formation
- diffraction
- absorption
 |
The correct answer is b, shadow formation. The model of light as straight rays explains how shadows form. The body blocks light from reaching whatever is behind it. 
|

