- You see balance beam with a length of 1 m. The fulcrum is 0.25 m from one end and there is a 10 kg bag of flour 0.75 m from the same end. How much torque does the bag create?
- 24.5 N m
- 49 N m
- 73.5 N m
- 196 N m
- A 5 kg box sits on one end of a balance beam of length 1 m. The fulcrum is in the middle. How far from the fulcrum would you have to place a second 10 kg box to balance the system?
- 0.25 m
- 0.5 m
- 0.75 m
- 1 m
- A 35 kg lighting fixture hangs from a church ceiling by a metal cable rated for a tension of 1,000 lb. What is the cable’s safety factor? (1 lb is 4.45 N.)
- 4
- 7.9
- 13
- 28
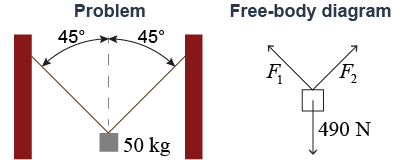
- A 50 kg mass is suspended from two identical cables, each at an angle of 45° from the vertical. Which statement correctly describes the magnitudes of the forces F1 and F2 exerted by the respective cables upon the hanging mass?
- F1 and F2 are equally strong, and each has a magnitude that is less than 245 N.
- F1 and F2 are equally strong, and each has a magnitude that equals 245 N.
- F1 and F2 are equally strong, and each has a magnitude that is greater than 245 N.
- You cannot choose between A, B, and C without more information.
- Which of the following expressions most nearly equals one pound-foot of torque in SI units? (Use the following conversion factors: 1 ft = 0.30 m and 1 lb = 4.45 N.)
- 0.07 N m
- 1.3 N m
- 4.75 N m
- 14.8 N m
| | 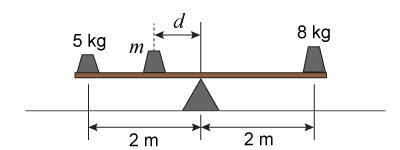
- A lightweight beam, 4 m long, is supported by a fulcrum at the midpoint. A 5 kg mass rests on the beam’s left end, and a 8 kg mass rests on the right end. A third object, of mass m, is to be placed a distance d to the left of the fulcrum in order to level the beam. Which mass-and-distance pair will do this?
- m = 12 kg and d = 0.5 m
- m = 10 kg and d = 1.0 m
- m = 12 kg and d = 1.0 m
- m = 3 kg and d = 1.0 m
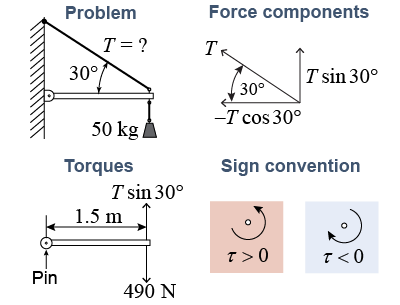
- A lightweight beam, 1.5 m long, is attached to a wall with a frictionless pin at one end and a cable at the other. The cable length allows the beam to hang horizontally, as shown. A 50 kg mass is suspended from the end of the beam that is attached to the cable. Which of the following equations best describes rotational equilibrium about the frictionless pin? (Assume that the beam’s mass is negligible.)
- T sin 30° + 490 N = 0
- T sin 30° − 490 N = 0
- T cos 30° + 490 N = 0
- T cos 30° − 490 N = 0
- Which of the following statements correctly describes the forces and torques on objects in statics problems?
- The net force upon an object of interest is zero, but the net torque may be nonzero.
- The net torque is zero, but the net force may be nonzero.
- The net force and the net torque upon an object of interest must both be zero.
- Neither the net force nor the net torque can be zero.
|

