|
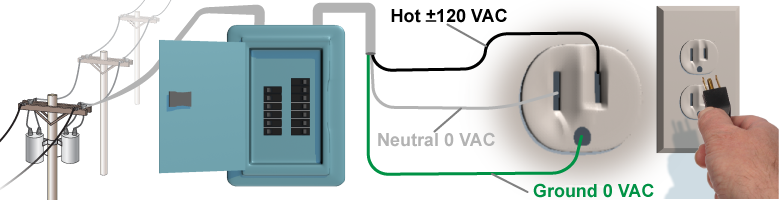
 The 120 VAC electricity comes into a typical home or building through a circuit breaker panel. The circuit breakers protect against wires overheating and causing fires. A 20 A breaker opens the circuit if the current exceeds 20 A for more than about a second. A typical circuit breaker panel has 15 A, 20 A, and 30 A breakers because the wires in a house are different sizes to safely carry different amounts of current.
The 120 VAC electricity comes into a typical home or building through a circuit breaker panel. The circuit breakers protect against wires overheating and causing fires. A 20 A breaker opens the circuit if the current exceeds 20 A for more than about a second. A typical circuit breaker panel has 15 A, 20 A, and 30 A breakers because the wires in a house are different sizes to safely carry different amounts of current. 
|
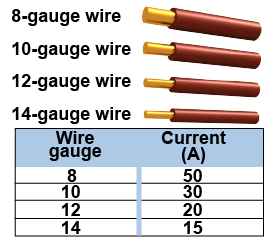
Electrical appliances such as a saw or hair dryer may draw up to 20 A of current. Outlet circuits are typically wired with 12-gauge wire that can carry 20 A and they are connected through a 20 A circuit breaker. Light bulbs use less than 1 A each. Light circuits are typically wired with 14-gauge wire that can carry 15 A and they are connected through a 15 A circuit breaker. High-power devices such as an electric stove (50 A) or electric dryer (30 A) use special shaped plugs connected with 8- or 10-gauge wire. 
|
|
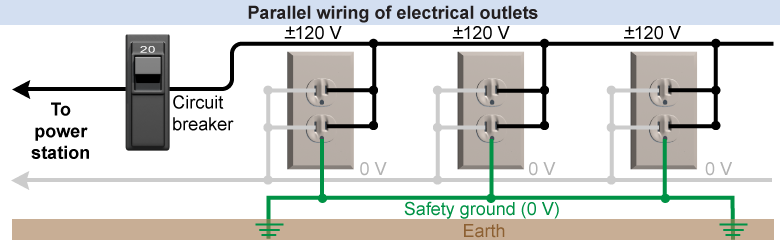
Electric power in homes and buildings is distributed through parallel circuits. The diagram shows a typical outlet circuit. Each outlet, or receptacle, has three wires: hot (black), neutral (white), and ground (green). The hot wire is connected to 120 VAC through the circuit breaker. The neutral wire is connected to zero volts. When you plug something in, current flows in and out of the hot wire, through your appliance (doing work) and back through the neutral wire. The ground wire is for safety and is connected to the ground (0 V) near your house. If there is a short circuit in your appliance, the current flows through the ground wire rather than through you. 
|
|
| |
|

