- Which is the best choice for reliably producing sound with a standardized frequency, a guitar string, a tuning fork, a bottle half-filled with water, or a resonance tube?
 Why must you adjust the length of a resonance tube in order for it to come into resonance with an external sound, such as from a tuning fork? Why must you adjust the length of a resonance tube in order for it to come into resonance with an external sound, such as from a tuning fork?
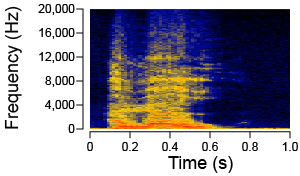
 The chart of the frequency spectrum for a human voice is shown here. How would the chart change if the person spoke more quietly? The chart of the frequency spectrum for a human voice is shown here. How would the chart change if the person spoke more quietly?
 Sasha and Alicia are swinging on the playground. Describe visually what you would see if the two girls were swinging in phase, 90° out of phase, and 180° out of phase. Sasha and Alicia are swinging on the playground. Describe visually what you would see if the two girls were swinging in phase, 90° out of phase, and 180° out of phase.
 Giovanni is blind but his hearing has perfect pitch. How can he tell quickly if a marching band is marching toward or away from him? Giovanni is blind but his hearing has perfect pitch. How can he tell quickly if a marching band is marching toward or away from him?
 A stationary observer hears the frequency of a horn of an approaching train as 333 Hz rather than the actual 300 Hz. If the train approached twice as fast, would the observed frequency decrease, increase, or stay the same? A stationary observer hears the frequency of a horn of an approaching train as 333 Hz rather than the actual 300 Hz. If the train approached twice as fast, would the observed frequency decrease, increase, or stay the same?
 A piano tuner listens to the beats between two strings played simultaneously to tell whether they are matched in frequency. What property of the beats tells the tuner that the two strings are perfectly in tune? A piano tuner listens to the beats between two strings played simultaneously to tell whether they are matched in frequency. What property of the beats tells the tuner that the two strings are perfectly in tune?
 Define the term harmonic in the context of frequencies of sound. Describe how the characteristic sounds of different instruments, such as a guitar and a piano, come from harmonics. Define the term harmonic in the context of frequencies of sound. Describe how the characteristic sounds of different instruments, such as a guitar and a piano, come from harmonics.
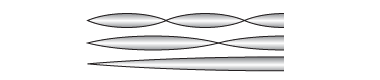
- The standing wave patterns in the diagram represent resonances of which kind of system?
- a pipe with two open ends
- a pipe with two closed ends
- a pipe with one open and one closed end
| |
 A sound wave has a wavelength of 0.96 m. How many times does this wave cause your eardrum to oscillate back and forth in 1 s? A sound wave has a wavelength of 0.96 m. How many times does this wave cause your eardrum to oscillate back and forth in 1 s?

 Two students use a spectrum analyzer to measure the frequency of the siren of a fire truck as it moves toward then away from them. They measured the frequency as 2,655 Hz when the fire truck was approaching (measurement “A”) and 2,362 Hz as the fire truck we receding (“B”). Two students use a spectrum analyzer to measure the frequency of the siren of a fire truck as it moves toward then away from them. They measured the frequency as 2,655 Hz when the fire truck was approaching (measurement “A”) and 2,362 Hz as the fire truck we receding (“B”).
- Why were the two frequency measurements different?
- If you were a firefighter riding on the truck, what would you observe to be the frequency of the siren?
- Calculate the speed of the fire truck.
 An orchestral oboist sounds the note “A” at 440 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, what is the wavelength of the note? An orchestral oboist sounds the note “A” at 440 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, what is the wavelength of the note?
 What is the wavelength of (a) a 100 Hz, (b) a 200 Hz, and (c) a 400 Hz sound wave in air? What is the wavelength of (a) a 100 Hz, (b) a 200 Hz, and (c) a 400 Hz sound wave in air?
 Joseph wears ear protection at work because machinery in his work environment creates sounds up to 110 decibels (110 dB). Safety regulations do not allow regular exposure to sounds above 90 dB. Joseph wears ear protection at work because machinery in his work environment creates sounds up to 110 decibels (110 dB). Safety regulations do not allow regular exposure to sounds above 90 dB.
- By how many decibels must Joseph’s ear protection reduce the sound of the machinery?
- By what factor is the amplitude of the sound wave reduced?
 You are standing on the sidewalk. A car approaches while playing a musical note from a loudspeaker on its roof. The note being played is middle C (f = 264 Hz), but you hear the note as C#—the next-highest note on a piano, with a frequency of 280 Hz. How fast is the car moving? You are standing on the sidewalk. A car approaches while playing a musical note from a loudspeaker on its roof. The note being played is middle C (f = 264 Hz), but you hear the note as C#—the next-highest note on a piano, with a frequency of 280 Hz. How fast is the car moving?
(Assume the sound speed vs is 343 m/s.)
 Sound travels at a speed of 1,490 m/s in sea water at 10°C, compared to traveling at 343 m/s in air. Sound travels at a speed of 1,490 m/s in sea water at 10°C, compared to traveling at 343 m/s in air.
- Calculate the wavelength of a 440 Hz sound in water and air. How do they compare?
- Consider the sound made by a meteor hitting the surface of the ocean. How far away is the impact point if the sound is detected in the water 112 s before it is detected in the air?
|

