| | Essential questions | | What is a sound wave?
What are the properties of sound waves? | |
|
Sound waves are traveling oscillations of air pressure. This interactive simulation allows you to determine the amplitude, wavelength, and frequency of some typical musical notes by matching the waveform in both time and space. 
|
Part 1: Matching the parameters of a sound wave
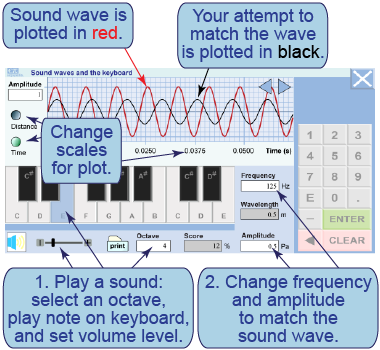 The red wave is the sound you are hearing, which you select with the piano keyboard keys. The black wave corresponds to the frequency, wavelength, and amplitude you set in the data boxes. The score is a percentage similarity between the red sound wave and the black wave with which you are trying to match it. The volume slider adjusts the volume of the sound (red wave). You will have to change the horizontal axis between time and length to determine both the frequency and the wavelength.
The red wave is the sound you are hearing, which you select with the piano keyboard keys. The black wave corresponds to the frequency, wavelength, and amplitude you set in the data boxes. The score is a percentage similarity between the red sound wave and the black wave with which you are trying to match it. The volume slider adjusts the volume of the sound (red wave). You will have to change the horizontal axis between time and length to determine both the frequency and the wavelength. - Choose a note and adjust your computer speakers so you can hear it.
- Set the time and amplitude values on the graph until you can see at least a few cycles of the sound wave.
- While time t is plotted on the horizontal axis, see whether you can make the black wave match the red sound wave by adjusting the frequency and amplitude.
- Switch to distance for the horizontal axis. Match your black wave to the red sound wave by adjusting the wavelength and amplitude. A good match has a score of greater than 95%. You must match both frequency and wavelength to score 100%.
- What is the frequency and wavelength of the note “C” on the left-hand side of the keyboard?
- Describe how the observed wave varies with loudness.
- Determine the frequency and wavelength for at least four different sounds.
- From your data, discuss possible relationships between frequency and wavelength with your lab partners. Propose and test an equation that expresses your hypothetical relationship.
- Using authoritative print or digital resources, research the value for the frequency of the note “A” in orchestral tuning. What is its accepted value and variation? Explain the origin of any variations.

|
In this interactive element, you will play the notes of a keyboard and match the properties of the sound (frequency, wavelength, and amplitude) related to each note.
|
Part 2: Going further with octaves
- Devise and conduct an experiment to determine what happens to the frequency and wavelength of sound when you set the octave to different values. Note that the octave can only be set to positive integers.
- What do you conclude occurs by setting different octaves?
- How does this fit with your prior knowledge of music?

| |
| |
|

