Match each word to the sentence where it best fits.
| moment of inertia | | translation | | rotation | | axis | | revolution | | linear momentum | | angular momentum | | rotational inertia | | conservation of angular momentum | | center of mass | |
- The product of mass and velocity is also called _______.
- The motion of a spinning wheel is called _______.
- It is important to have your _______ located directly over your feet or you might fall over!
- It is hard to stop a spinning carousel because it has a lot of _______.
- The central line about which a gyroscope rotates is called its _______ of rotation.
- When a spaceship moves from here to there the motion is called _______.
- Any object that is spinning or rotating has _______.
- _______ holds in the absence of net, external torques.
- The rotational analog to mass is _______.
| rotational energy | | precession | |
- A ball rolling downhill possesses _______ while a ball sliding downhill does not.
- A horizontally spinning gyroscope slowly spins around a vertical axis in a phenomenon called _______.
- How does rotational inertia differ from linear inertia?
- Compare and contrast rotation and revolution from the point of view of angular motion. Then give an astronomical example of each.
- Two objects have the same mass. Must they have the same rotational inertia?
| | - For each of the following, determine whether the motion is rotational or translational. If rotational motion is included, then identify whether it is rotation, revolution, or both.
- a car wheel when the car is being driven on the highway
- an electric motor lifting a projector screen
- a falling rock
- a gyroscope on a table
- a car wheel when the driver slams on the brakes and the car skids as a result
- an orbiting satellite
- the Earth in its usual motion
- Based on the units of each of the following quantities, determine whether each is a measurement of linear or angular momentum.
- 10 kg m/s
- 13 kg m2/s
- (15 kg/s)(10 m)
- (13 kg m)(11 m/s)
- (11 m2/s)(5 kg/m)
- Write a sentence explaining the relationship between rotational inertia and the moment of inertia. Then write a similar sentence for inertia and mass.
- A spinning object is modified so that it doubles its moment of inertia but its angular velocity does not change. What happens to its angular momentum?
- If a gyroscope were to fall over, would its angular momentum change?
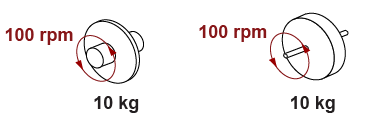
- The two shapes shown have the same mass, diameter, and rotational speed. Which is true and why?
- Both have the same angular inertia because they have the same mass and speed.
- The thin wheel has more angular inertia because its mass is concentrated near the axis of rotation.
- The thick wheel has more angular inertia because its mass is distributed farther from the axis of rotation.
- For each of the following objects undergoing rotational motion, describe where the axis of rotation is.
- a planet rotating
- a planet revolving
- a pencil stood on end and falling over
- a spinning top
- a satellite orbiting above the equator
|

