|
| Essential questions | | How do we predict the effect of forces on motion?
How is the second law used? | |
|
Motion changes through the action of forces. The changes occur through acceleration because acceleration is a direct consequence of a nonzero net force. Models of motion start by calculating the acceleration from a knowledge of forces. Acceleration is used to determine changes in velocity, which are used to determine changes in position. 
|
Part 1: Modeling the action of a force
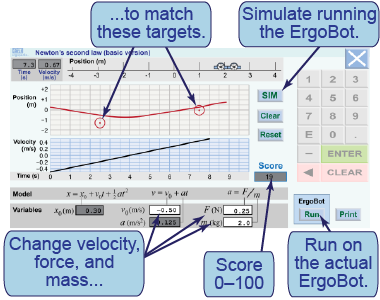
- The interactive model of Newton’s second law shows position and velocity versus time graphs. Red circles on the position versus time graph are “targets.” Adjust the initial parameters—initial velocity v0, force F, and mass m—so that the curves hit both targets.
- [SIM] starts the simulation. [Stop] stops it without changing values. [Clear] resets all variables to zero.
- Enter values in the white boxes. The top score of 100 is achieved by hitting the center of each target.
- Try another problem: Press [Reset] to reset all variables and set new targets.
- Compare how 1 N of force affects the motion of a 5 kg ErgoBot versus a 0.2 kg ErgoBot.
- Describe the connection between force and acceleration.
- If you double both the force and mass, how are the resulting position and velocity graphs affected? Why?

|
|
In this interactive simulation, you will create a model for the motion of the ErgoBot by adjusting the values of the initial velocity, force, and mass. The goal is to select an appropriate force that will cause the ErgoBot’s motion to pass through the target circles on the position versus time graph.
|
Part 2: Dynamic modeling
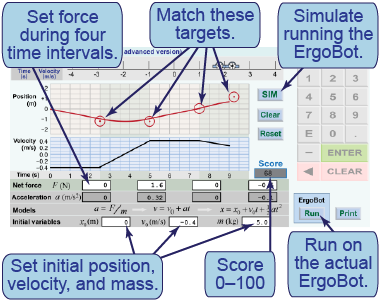
- The second model allows you to set the force for four different time intervals, each two-and-a-half seconds (2.5 s) long.
- In this model, unlike the first, you can set the starting position (x0) in addition to the initial velocity, mass, and four periods of force.
- Try to hit the centers of the four red target circles.
- Which sections of the graphs are curved and which are linear? Why?
- If the ErgoBot’s mass is doubled, how is the displacement affected?

|
|
In this interactive simulation, you will create a model for the motion of the ErgoBot by adjusting the values of the initial position, initial velocity, mass, and four forces. The goal is to select appropriates force that will cause the ErgoBot’s motion to pass through the target circles on the position versus time graph.
|

