|
The first and second laws apply to single objects and the forces that act on them. Newton’s third law of motion addresses interactions between objects, or between objects and the environment. Every exchange of force comes from the interaction of at least two objects. For example, throwing a ball is an interaction between the ball and you. The third law says that forces in nature always occur in pairs, like the top and bottom of a sheet of paper. You cannot have one without the other. When you apply an action force to throw a ball, you feel the reaction force from the ball pushing back against your hand. 
|

|
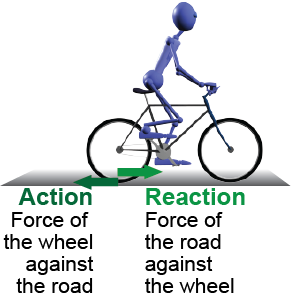 Consider riding a bicycle. Pushing on the pedals causes a force to be transmitted through the chain to the wheel, which pushes against the ground. This force acts against the ground. What force acts against the bicycle to move you? The answer is the reaction force of the ground acting against your wheel. This reaction is the equal and opposite partner of the action force of your wheel against the ground. The reaction force is what moves you. The same is true of driving and walking. We push against the ground, but it is the equal and opposite reaction of the ground pushing back that actually moves us.
Consider riding a bicycle. Pushing on the pedals causes a force to be transmitted through the chain to the wheel, which pushes against the ground. This force acts against the ground. What force acts against the bicycle to move you? The answer is the reaction force of the ground acting against your wheel. This reaction is the equal and opposite partner of the action force of your wheel against the ground. The reaction force is what moves you. The same is true of driving and walking. We push against the ground, but it is the equal and opposite reaction of the ground pushing back that actually moves us. 
|

|
The normal forces that occur between objects and supporting surfaces are also reaction forces. Consider a box on the table. The box pushes down on the table with a force equal to its weight. That force acts on the table. The reaction force is the table acting back up on the box. The forces that hold objects up are reaction forces. 
|
Don’t get confused about which force is the action and which is the reaction. The words action and reaction are just labels and it does not matter which is which. - All forces come in pairs. If one is the action, then the other is the reaction.
- Action–reaction forces are always exactly equal in strength and opposite in direction.
- The action and reaction forces always act on different objects, so they never cancel each other out. They also act simultaneously with each other.

|
Michael wants to jump higher. To do so, he must apply a more forceful push on the ground. This in turn will cause a greater ___________ force into his body, propelling him upward. - friction
- gravitational
- reaction
- magnetic
 |
The answer is c. For every force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. 
|

