|
Single forces do not always change an object’s motion because many forces usually act on the same object at the same time. The net force is the total, or sum, of all forces acting on an object. Objects respond to the net force instead of individual forces. Forces may cancel each other out when multiple forces act in different or opposite directions. Stationary objects such as buildings and bridges stand still because of zero net force, not because there are no forces. 
|
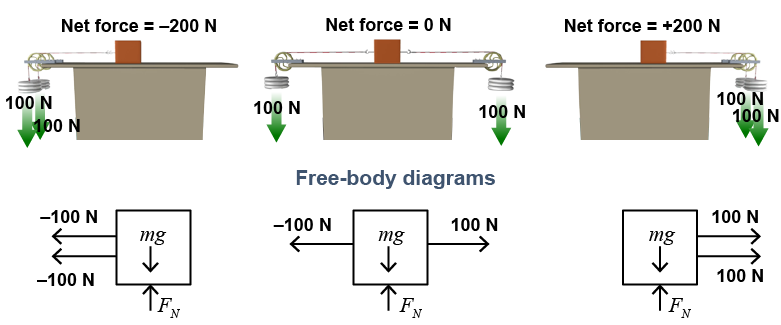
|
Two 100 N forces act horizontally on the box in the diagram above. The net force is different in each of the three situations. The free-body diagrams show that the net force in the horizontal direction is −200 N to the left in one case, zero in another, and +200 N to the right in the third case. The net force in the vertical direction is zero. 
|

|
The direction of a force matters when determining the net force. Force, like position, is a vector. In one-dimensional problems positive and negative signs are used to indicate direction. Forces should be assigned positive and negative values that correspond to direction. 
|
When solving problems involving forces and free-body diagrams, you must choose which direction is positive. The opposite direction then becomes negative. Diagrams are often chosen such that right and up is positive and left or down is negative. The choice, however, is arbitrary and it may be easier for some problems to choose differently. Once you choose the positive direction, you must be consistent throughout the entire solution process. 
|
In most physics problems you will need to consider the net force separately in each of the perpendicular directions. For example, a 200 N upward force cannot cancel with a −200 N force to the left because these forces do not act along the same line. The net force may be different in different directions. In the example above, the vertical net force is zero but the net force in the horizontal direction may not be zero. 
|
Nina is pulling on a box with a force of 250 N, but the box isn’t moving. What is the force of friction on the box? - 0 N
- 250 N
- 500 N
- Not enough information
 |
The answer is b, 250 N. If the box is not moving, then there is no net force on it. This means that Nina’s pulling force must be canceled out by friction. 
|

