- Research and describe three energy flow diagrams for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
- List five ways in which food you buy in a grocery store has an “energy content” other than the actual calories your body gets from eating the food.
- How does the Sun’s energy reach us?
- Mercury thermometers, once common in science classrooms, have been largely replaced due to safety concerns. The “fire diamond” and the global harmonization system (GHS) are two methods used to label a mercury hazard. Locate and reproduce images of both labels and evaluate their relative strengths and weaknesses.
 Identify the only career in the following list that does not require any knowledge of physics: optometrist, petroleum engineer, astronomer, industrial engineer, grocer, robotics designer, architect, and physical therapist. Identify the only career in the following list that does not require any knowledge of physics: optometrist, petroleum engineer, astronomer, industrial engineer, grocer, robotics designer, architect, and physical therapist.
 Research a physics-related career and develop a class presentation. The presentation should use digital media (text, graphics, audio, etc.) to illustrate your findings and provide interest. Research a physics-related career and develop a class presentation. The presentation should use digital media (text, graphics, audio, etc.) to illustrate your findings and provide interest.
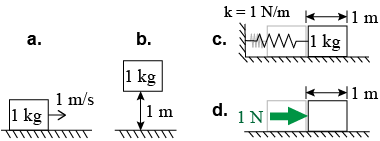
- Rank the following scenarios in order of most energy to least energy.
- 1 kg block moving at 1 m/s on the ground
- 1 kg block at rest 1 m above the ground
- 1 kg block at rest on the ground but attached to a spring with k = 1 N/m that is stretched 1 m
- the work done to push the block a distance of 1 m with a force of 1 N
 What is the elastic potential energy of a rubber band with a spring constant of 25.0 N/m if it is stretched by 10.0 cm from its original length? What is the elastic potential energy of a rubber band with a spring constant of 25.0 N/m if it is stretched by 10.0 cm from its original length?
 If a box’s mass is cut in half, but the box is raised to a height four times higher, how does its potential energy change? If a box’s mass is cut in half, but the box is raised to a height four times higher, how does its potential energy change?
| | 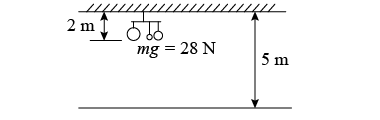
 A mobile that weighs 28 N is hanging 2 m below a ceiling that is 5 m high. What is its potential energy with respect to the floor, the ceiling, and a point at the same height as the mobile? A mobile that weighs 28 N is hanging 2 m below a ceiling that is 5 m high. What is its potential energy with respect to the floor, the ceiling, and a point at the same height as the mobile?
 What is the kinetic energy of a 6 kg bird moving at a speed of 15 m/s? What is the kinetic energy of a 6 kg bird moving at a speed of 15 m/s?
 What is the largest force that an energy source containing 100 J can exert continuously over a distance of 25 m? What is the largest force that an energy source containing 100 J can exert continuously over a distance of 25 m? | a. | 0.25 N | | b. | 4 N | | c. | 25 N | | d. | 2,500 N |
 At what height would a 15 kg bird have a potential energy of 2,400 J? At what height would a 15 kg bird have a potential energy of 2,400 J?
 If you double the speed and mass of an object how does its kinetic energy change? If you double the speed and mass of an object how does its kinetic energy change?
 A 1 kg ball and a 9 kg ball have the same Ek. Compare their speeds. A 1 kg ball and a 9 kg ball have the same Ek. Compare their speeds.
 A small airplane has a kinetic energy of 5,000,000 J when it travels at 100 m/s. What is its mass? A small airplane has a kinetic energy of 5,000,000 J when it travels at 100 m/s. What is its mass?
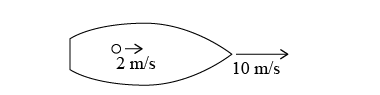
 A ball with a mass of 150 g rolls due north along the deck of an ocean liner at a speed of 2.0 m/s. The ocean liner is also moving north, with a speed of 10.0 m/s relative to a nearby island. A ball with a mass of 150 g rolls due north along the deck of an ocean liner at a speed of 2.0 m/s. The ocean liner is also moving north, with a speed of 10.0 m/s relative to a nearby island.
- What is the kinetic energy of the ball as measured from the reference frame of the ocean liner?
- What is the kinetic energy of the ball as measured from the reference frame of the island?
 How far is a spring extended if it has 1.0 J of potential energy and its spring constant is 1,000 N/m? How far is a spring extended if it has 1.0 J of potential energy and its spring constant is 1,000 N/m?
 How much work do you do when you push a 400 kg car for 6 m with a force of 300 N? What is the car’s final speed if all your work became kinetic energy? How much work do you do when you push a 400 kg car for 6 m with a force of 300 N? What is the car’s final speed if all your work became kinetic energy?
 Relative to sea level, how much total mechanical energy does a plane with mass of 1,000 kg have when it moves at 235 m/s at an altitude of 2 km above sea level? Relative to sea level, how much total mechanical energy does a plane with mass of 1,000 kg have when it moves at 235 m/s at an altitude of 2 km above sea level?
|

