- What is the magnitude of a force that is required to keep a spring with a spring constant of 500 N/m compressed 0.3 m from its starting point?
- How far must a 100 N/m spring stretch to hold up a 4 kg box?
- What is the spring constant of a spring that exerts a 56 N force after it is stretched 0.16 m?

- How much does a front suspension system that has a spring constant of 50,000 N/m compress when it supports forces of 1,500 N from a bike and rider?
- What is the force exerted by a spring where k = 400 N/m when it is stretched 0.6 m in the positive direction?
- How far does a spring stretch to support a 50 N weight if it has a spring constant of 3,000 N/m?
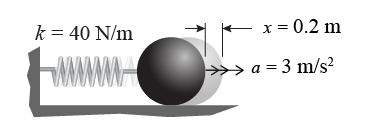
- An object of unknown mass is connected to a spring with k = 40 N/m. When the spring is compressed 0.2 m, the object accelerates at 3 m/s2. What is its mass?
- Resistance bands used for exercise are essentially large rubber bands that act similarly to a spring. If Madison can supply a maximum force of 500 N how far will she be able to stretch a resistance band that has k = 400 N/m?
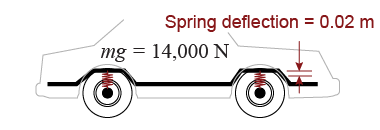
- A 14,000 N car is supported by four springs. If each spring is deflected 0.02 m, what is the spring constant?
- A 400 N force causes a spring to compress 0.2 m. What is the spring constant of the spring?
| | - When a bow is at its most stretched it can accelerate a 0.5 kg arrow at 80 m/s2. If the spring constant is k = 100 N/m, how far has the bow been stretched?
- When testing a spring, you find that it takes 20 N of force to compress the spring by 10 cm. What is the spring constant for this spring?
 How far does a 5,000 N/m spring stretch when supporting a 300 N weight? How far does a 5,000 N/m spring stretch when supporting a 300 N weight?
 You hang a 10 N mass from a scale and find that this makes the spring stretch 0.04 m. What is this spring’s spring constant? You hang a 10 N mass from a scale and find that this makes the spring stretch 0.04 m. What is this spring’s spring constant?
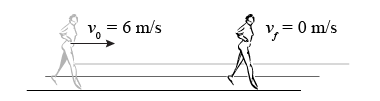
 The coefficient of kinetic friction between newly waxed floors and socks is 0.12. How far does Laura slide if she has an initial speed of 6 m/s? The coefficient of kinetic friction between newly waxed floors and socks is 0.12. How far does Laura slide if she has an initial speed of 6 m/s?
 What is the magnitude of the acceleration caused by the force of kinetic friction acting on a box sliding across a level table? The coefficient of friction is μk = 0.3. What is the magnitude of the acceleration caused by the force of kinetic friction acting on a box sliding across a level table? The coefficient of friction is μk = 0.3.
 How far does a box travel until it is stopped by friction if it has an initial velocity of 8 m/s and there is a coefficient of friction of 0.102? How far does a box travel until it is stopped by friction if it has an initial velocity of 8 m/s and there is a coefficient of friction of 0.102?
- How many 20 N bricks should you add to increase the friction force on a cart by 80 N if the coefficient of friction is 0.8?
 A 12 kg computer is sitting on a table and the coefficient of static friction between the computer and the table is 0.7. If the computer is pushed with a horizontal 30 N force, what is the actual force of static friction between the computer and the table? A 12 kg computer is sitting on a table and the coefficient of static friction between the computer and the table is 0.7. If the computer is pushed with a horizontal 30 N force, what is the actual force of static friction between the computer and the table?
- A box of oranges lies in the back of a truck. The coefficient of static friction is 0.5. If the truck accelerates from 20 m/s to 10 m/s in 3 s, will the box slide?
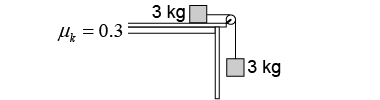
- Two identical 3 kg masses are connected by a string that passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in the drawing above. If the coefficient of friction is 0.3, what is the acceleration of the hanging block?
|

