- A 100 N wood friction block is on top of concrete. What is the net force on the block when sliding on the concrete if there is a 75 N force pushing it?
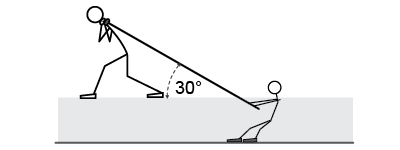
- Katie weighs 600 N, wears wooden shoes, and is being pulled along the wood floor of the orchestra pit by her mother using an 800 N force at a 30° angle as shown. Find the force of friction between Katie and the floor and the net force acting on Katie. Assume that the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3 for wood-on-wood.
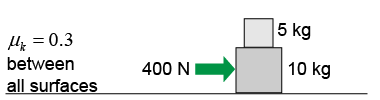
- A 10 kg block and a 5 kg block are resting on each other on a flat surface. The heavier block is pushed with a 400 N force.
- Draw the free-body diagram of the 10 kg block.
- What is the net force acting on the 10 kg block? Give the x and y components.
- What is the net force acing on the 5 kg block in each of the x and y directions?
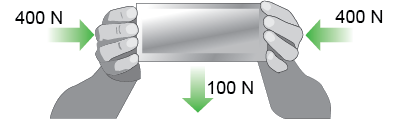
- A 100 N tin box is prevented from falling by holding it on both sides. If the pushing forces are 400 N each, what is the coefficient of friction?
- How much work does the kinetic friction force do on Jesse, who weighs 720 N, as he slides for 4 m on a surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.4?
- By what factor does stopping distance change if the coefficient of friction is doubled?
- If the friction force is 450 N when the coefficient of friction is 0.3, what is the normal force?
 What is the coefficient of kinetic friction if a car going at 20 m/s stops in 50 m? What is the coefficient of kinetic friction if a car going at 20 m/s stops in 50 m?
| |  Which of the following sentences is closest to the meaning of the equation μk = Ff / FN? Which of the following sentences is closest to the meaning of the equation μk = Ff / FN? - The force of friction is the coefficient of friction divided by the normal force.
- The coefficient of friction is the ratio of the friction force to the normal force.
- The normal force creates a friction force when multiplied by a coefficient of friction.
 A 3 kg rubber block is resting on wet concrete. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3. What is the minimum force that must be applied to the block to make the block begin to accelerate? A 3 kg rubber block is resting on wet concrete. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3. What is the minimum force that must be applied to the block to make the block begin to accelerate?
 A crate of physics textbooks is sliding across the room at 18 m/s. What is the coefficient of friction that causes it to come to a stop in 12 s? A crate of physics textbooks is sliding across the room at 18 m/s. What is the coefficient of friction that causes it to come to a stop in 12 s?
 A 4 kg box sits in the back of your 1,400 kg car with a coefficient of static friction between the box and your car of 0.4. The car is traveling at 15 m/s. What is the minimum stopping distance that can be obtained without the box sliding? A 4 kg box sits in the back of your 1,400 kg car with a coefficient of static friction between the box and your car of 0.4. The car is traveling at 15 m/s. What is the minimum stopping distance that can be obtained without the box sliding?
 The police find skid marks that are 80 m long left by a 1,300 kg car. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the road is 0.6. How fast was the car going before the brakes were applied? If the speed limit is 60 mph, was the driver speeding? The police find skid marks that are 80 m long left by a 1,300 kg car. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the road is 0.6. How fast was the car going before the brakes were applied? If the speed limit is 60 mph, was the driver speeding?
 A cart is propelled by an engine so that when it is on a surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.3 it travels at constant velocity. What is the acceleration of the cart on a surface with a coefficient of 0.2 assuming the force is the same? A cart is propelled by an engine so that when it is on a surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.3 it travels at constant velocity. What is the acceleration of the cart on a surface with a coefficient of 0.2 assuming the force is the same?
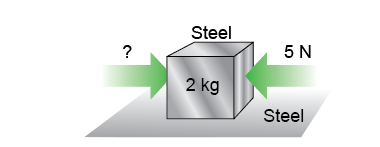
 How much force is required to start moving a 2 kg block of steel on dry steel if there is a 5 N force opposing you? How much is required to keep it from slowing down assuming the opposition force remains? (For steel on dry steel, μs = 0.8 and μk = 0.5.) How much force is required to start moving a 2 kg block of steel on dry steel if there is a 5 N force opposing you? How much is required to keep it from slowing down assuming the opposition force remains? (For steel on dry steel, μs = 0.8 and μk = 0.5.)
 The coefficient of friction between a 0.17 kg puck and and the ice is μk = 0.15. If the puck leaves a hockey stick traveling at 20 m/s, what is its speed when it reaches the goalie 15 m away? How much time does the goalie have to react? Assume the puck travels on the ice the whole time. The coefficient of friction between a 0.17 kg puck and and the ice is μk = 0.15. If the puck leaves a hockey stick traveling at 20 m/s, what is its speed when it reaches the goalie 15 m away? How much time does the goalie have to react? Assume the puck travels on the ice the whole time.
|

