- Which of the following equations best represents the following statement?
“In a transformer, the ratio of the secondary to primary voltage equals the ratio of the number of secondary to primary coils.” -
-
-
-
- Siegfried placed a 10−5 T bar magnet inside a 56-coil solenoid of length 4 cm and diameter 1 cm. His lab partner, Rob, then measured the current through the solenoid’s wire.
- What is the value of the current Rob measures?
- What can Siegfried do to change the value of the current Rob will observe?
 Lehi makes his own transformer by winding 10 loops of wire around one side of an iron rod and 20 loops of wire on the other side. Then he connects a DC (constant voltage) battery to the first coil. After he connects the battery, he checks the voltage coming out of the second coil, but there is no voltage. What did he do wrong? Lehi makes his own transformer by winding 10 loops of wire around one side of an iron rod and 20 loops of wire on the other side. Then he connects a DC (constant voltage) battery to the first coil. After he connects the battery, he checks the voltage coming out of the second coil, but there is no voltage. What did he do wrong?
 A constant magnetic field points upward from the floor to the ceiling everywhere in the room. There are three loops of wire: A, B, and C. Loop A is flat on a table, B is perpendicular to the table, and C is at a 45° angle to the table. A constant magnetic field points upward from the floor to the ceiling everywhere in the room. There are three loops of wire: A, B, and C. Loop A is flat on a table, B is perpendicular to the table, and C is at a 45° angle to the table.
- List the loops in order of least to greatest magnetic flux.
- In which, if any, of the loops will an electric current be induced?
 A magnetic field points down and is decreasing in strength. The induced current in a wire loop on the top of a table will flow ___________ (clockwise, counterclockwise) when viewed from the top. A magnetic field points down and is decreasing in strength. The induced current in a wire loop on the top of a table will flow ___________ (clockwise, counterclockwise) when viewed from the top.
 A magnetic field points into the page and is increasing in strength. For a wire loop in the plane of the page, will the induced current flow clockwise or counterclockwise? A magnetic field points into the page and is increasing in strength. For a wire loop in the plane of the page, will the induced current flow clockwise or counterclockwise?
 When power plants generate electricity, they use a transformer to transmit the electricity through power lines at a low current to reduce power loss. Then a transformer at your house converts it back to the voltage that your appliances use. Which transformer is “step up” and which is “step down?” How do you know? When power plants generate electricity, they use a transformer to transmit the electricity through power lines at a low current to reduce power loss. Then a transformer at your house converts it back to the voltage that your appliances use. Which transformer is “step up” and which is “step down?” How do you know?
| |
- Which statement best expresses the following equation for the magnetic force on a moving, charged particle?
- The magnetic force is the product of charge, speed, magnetic field, and the sine of the angle between its velocity and the magnetic field.
- The magnetic field is the product of charge, speed, magnetic force, and the sine of the angle between its velocity and the magnetic field.
- The magnetic field is the sum of charge, speed, magnetic force, and the cosine of the angle between its velocity and the magnetic field.
- The magnetic force is the product of charge, speed, magnetic field, and the sine of the angle between its charge and its velocity.
- In a particle accelerator experiment, a particle produced by a collision was observed to move in a spiraling pattern. What property of the particle can you infer from this observation?
 In a particle accelerator experiment, two particles observed after a collision were moving in spirals—but rotating around their spirals in the opposite direction. What intrinsic property can you infer about the two particles? In a particle accelerator experiment, two particles observed after a collision were moving in spirals—but rotating around their spirals in the opposite direction. What intrinsic property can you infer about the two particles?
 Why is an image on the screen of a cathode ray tube affected by moving a horseshoe magnet near to it? Why is an image on the screen of a cathode ray tube affected by moving a horseshoe magnet near to it?
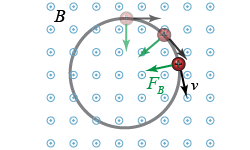
 This diagram shows a uniform magnetic field B emerging toward you from the plane of the page. It also shows a positively charged particle moving with velocity v. The charged particle experiences a force FB due to its motion within the field. This diagram shows a uniform magnetic field B emerging toward you from the plane of the page. It also shows a positively charged particle moving with velocity v. The charged particle experiences a force FB due to its motion within the field. - If you were using the right-hand rule for magnetic force on a moving charge, which of the labeled vectors would correspond to your thumb?
- Which of the labeled vectors would correspond to your index finger?
- Suppose the particle became negatively charged, but nothing else in the diagram changed. Which way would FB point?
- Suppose B reversed direction, but nothing else in the diagram changed. Which way would FB point?
|

