Match each word to the sentence where it best fits.
| sliding friction | | coefficient of rolling friction | | static friction | | coefficient of static friction | | coefficient of kinetic friction | | coefficient of kinetic friction | | rolling friction | | lubrication | | viscosity | | drag coefficient | |
- It is easier to swim through water than gelatin, because gelatin has a higher _______.
- The _______ is a ratio of the friction between two surfaces in contact that are not moving relative to each other to the normal force between them.
- The _______ is a ratio of the amount of friction between two surfaces in contact that are sliding relative to each other to the normal force between them.

- Where is the center of mass of a doughnut? Is it inside or outside the doughnut? How do you know?
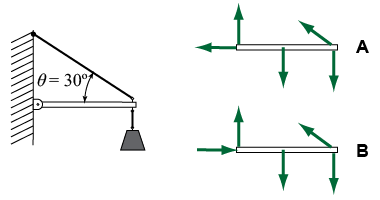
- Which of the two sketches is the correct free-body diagram of the horizontal arm holding the weight? Explain why the other is incorrect.
- What quantities sum to zero when a system is in equilibrium?
- You and your friend want to balance a teeter-totter, but your friend is much heavier than you. How can you balance it?
| | - What is the difference between mass and weight? What units of the metric system are used to describe them? What United States customary units are used?
 When you walk, you push on the ground. This exerts a force on the ground. What exerts a force on you to propel you forward? When you walk, you push on the ground. This exerts a force on the ground. What exerts a force on you to propel you forward?
- Two balls of equal mass collide. One of them experiences a 12 m/s2 acceleration at one moment. What acceleration does the other ball experience at the same moment?
- A 50,000 kg plane is flying at a constant velocity of 130 m/s. What is the net force that is acting on it?
- Can an object be moving when the net force acting on it is zero? If so, explain how this can be true.
- What is the reaction partner to the weight of an object sitting on a table? Is the reaction force the normal force of the table acting upward to hold the object up? If not, then what is the correct reaction force?
- Explain why action and reaction forces cannot cancel each other out.
- Jamayla and Iris are ice skating and standing next to each other. Jamayla pushes Iris and each then moves away from the other. Express what they just did using vocabulary from Newton’s laws.
 If every action has an equal and opposite reaction, then when you jump and gravity pulls you back down, it also pulls the Earth up to you. Why can’t you see this motion? If every action has an equal and opposite reaction, then when you jump and gravity pulls you back down, it also pulls the Earth up to you. Why can’t you see this motion?
 If you add mass to a car on a ramp the acceleration of the car does not increase proportional to the increase in mass. Why not? If you add mass to a car on a ramp the acceleration of the car does not increase proportional to the increase in mass. Why not?
 The tendency of a moving body to keep moving and a body at rest to stay at rest is described by the first of which set of principles? The tendency of a moving body to keep moving and a body at rest to stay at rest is described by the first of which set of principles?
 Why does it hurt more to kick a bowling ball than a beach ball? Why does it hurt more to kick a bowling ball than a beach ball?
 Which of Newton’s laws best explains why it hurts to punch someone? Which of Newton’s laws best explains why it hurts to punch someone?
 If, according to Newton’s third law, every reaction has an equal and opposite reaction, then how can motion ever occur? Wouldn’t every force be canceled out by its reaction force? If, according to Newton’s third law, every reaction has an equal and opposite reaction, then how can motion ever occur? Wouldn’t every force be canceled out by its reaction force?
|

