|
| Essential questions | | What happens when a wave hits an obstacle? | |
|
Waves interact with matter in four fundamental ways: reflection, refraction, diffraction, and absorption. This simulation allows you to see how each of these interactions affects waves of different frequency and wavelength. 
|
Part 1: Investigate reflection
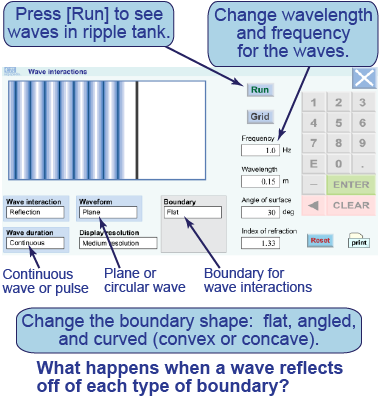 By default, the simulation will show continuous plane waves reflecting off of a flat surface.
By default, the simulation will show continuous plane waves reflecting off of a flat surface. - Press [Run] to watch the waves propagate.
- Change the wavelength and/or frequency (using the keypad) and press [Run] to see the new simulation.
- Repeat the simulation for three different boundaries (or reflecting surfaces): angled wall; curved, concave wall; and curved, convex wall. Press [Run] to watch each new simulation.
- Sketch a plane wave reflecting from a straight wall. How does the direction of the wave change?
- Sketch a plane wave reflecting from an angled wall. How does the direction of the wave change?
- Sketch a plane wave reflecting from a concave wall and a convex wall. Which one
diverges the wavefronts? Which one converges the wavefronts? 
|
|
In this interactive simulation of a ripple tank, you will explore wave interactions of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, and interference.
|
Part 2: Investigate refraction, diffraction, and interference
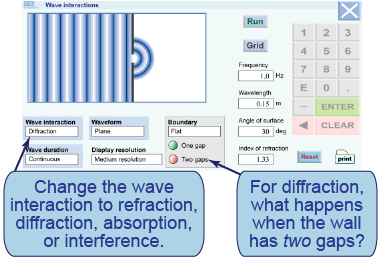
- Investigate refraction of plane waves for two cases: a flat boundary and an angled boundary.
- Investigate diffraction of plane waves for three cases: around a half wall and through a flat wall with either single or double gaps in its middle.
- Investigate diffraction further by varying the wavelength for the single-gap wall.
- Investigate absorption using a flat boundary.
- Investigate interference using two circular waves.
- Sketch the wavefronts refracted by the flat boundary. What happens to the direction and wavelength?
- Sketch wavefronts refracted by an angled boundary. What happens to direction and wavelength?
- Sketch the wavefronts for a plane wave passing by a half wall. Can you describe what you observe using the term
diffraction? Sketch the wavefronts passing through the single gap. Sketch the wavefronts passing through the double gap. Describe what you observe using the term interference. How does varying the wavelength change the way the waves diffract? Sketch the wavefronts before and after they interact with the absorbing material. What happens to the wave? Propose a hypothesis to explain what happens to the energy of the wave. Sketch the wavefronts for two circular waves. Where do the waves cancel each other out? 
|

