|
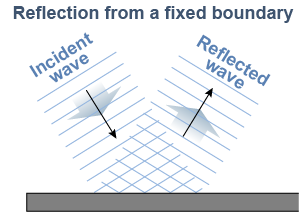 Reflection causes a wave to change direction and may also change the shape of its wavefront. Reflection occurs for both transverse and longitudinal waves. A plane wave encountering a straight boundary reflects in a new direction while keeping the same waveform. The same is true of a circular wave. A circular wave reflecting from a straight boundary will still be a circular wave.
Reflection causes a wave to change direction and may also change the shape of its wavefront. Reflection occurs for both transverse and longitudinal waves. A plane wave encountering a straight boundary reflects in a new direction while keeping the same waveform. The same is true of a circular wave. A circular wave reflecting from a straight boundary will still be a circular wave. 
|
Reflection occurs at boundaries where conditions change, such as the edge of a pool or the wall of a room. The end of a long, snaky spring can also be considered a boundary for waves on the spring since it represents a change of conditions. 
|

|
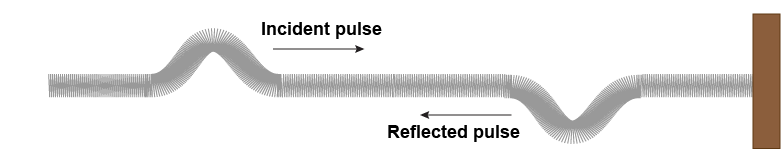
The kind of reflection that occurs at a boundary depends on whether the boundary is fixed or open. A fixed boundary does not move in response to the wave. A transverse wave pulse on a spring reflects onto the opposite side of the spring when encountering a fixed boundary. The free end of a spring is an open boundary. The end moves in response to a wave traveling along the spring. A wave pulse reflects back on the same side of the spring when encountering an open boundary. 
|
|
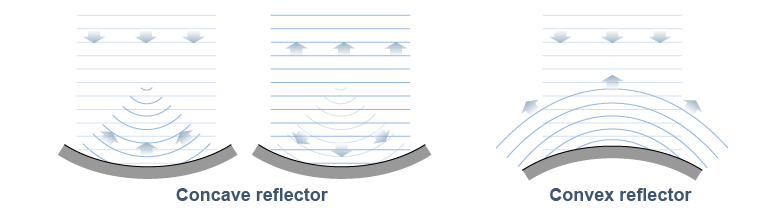
Curved boundaries can change the shape of a wave, altering its direction. A concave reflector can turn a plane wave into a circular wave that converges to a point. A circular wave reflecting off the same shape can turn into a plane wave. A convex reflector can turn a plane wave into a circular wave that diverges from a point. The convex shape can also turn a circular wave into another circular wave with a different curvature. Curved boundaries are extensively used in communications technology such as satellite dish receivers. 
|
|

