|
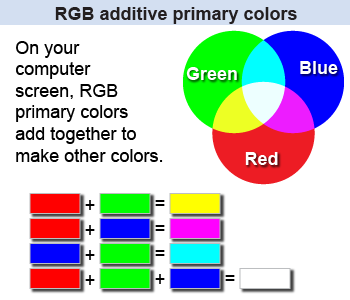 The three primary colors red, green, and blue are called the additive primary colors (RGB). The additive color process occurs in the lamps inside a computer projector or an LED computer or television screen. Each has a collection of tiny lamps—some red, some green, and some blue—that illuminate in relative intensity to create any color in the rainbow. When two adjacent, tiny pixels on your LED screen show blue and red, your eye sees them combined together as magenta. If blue, red, and green all illuminate next to each other, then your eye sees white light.
The three primary colors red, green, and blue are called the additive primary colors (RGB). The additive color process occurs in the lamps inside a computer projector or an LED computer or television screen. Each has a collection of tiny lamps—some red, some green, and some blue—that illuminate in relative intensity to create any color in the rainbow. When two adjacent, tiny pixels on your LED screen show blue and red, your eye sees them combined together as magenta. If blue, red, and green all illuminate next to each other, then your eye sees white light. 
|
 Digital images are made of tiny dots, or pixels, of color; a one megapixel image has one million dots. Each pixel in the image is captured by three tiny sensors in the camera, which, like the human eye, respond to red, green, or blue light. In turn, each sensor records a number from 0 to 255 corresponding to the intensity of the light it receives. A one megapixel digital image is a string of three million numbers that prescribe the intensity of red, green, and blue for each pixel. The maximum is assigned to 255 because computers use binary numbers and 28 = 256.
Digital images are made of tiny dots, or pixels, of color; a one megapixel image has one million dots. Each pixel in the image is captured by three tiny sensors in the camera, which, like the human eye, respond to red, green, or blue light. In turn, each sensor records a number from 0 to 255 corresponding to the intensity of the light it receives. A one megapixel digital image is a string of three million numbers that prescribe the intensity of red, green, and blue for each pixel. The maximum is assigned to 255 because computers use binary numbers and 28 = 256. 
 |
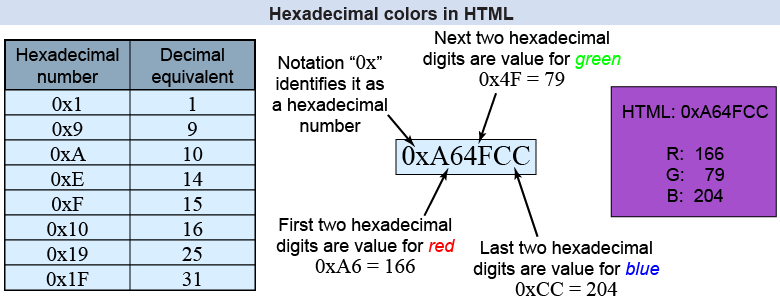 If you have ever written a web page in hypertext markup language (HTML), you might have tried to specify a color for a font or background in RGB. The most common method is to specify the brightness of each color from 0 (none) to 255 (brightest). Those are 256 different possible brightnesses for each color, because you have to remember to count zero, too! Another way of specifying numbers from zero to 255 is by using two–digit hexadecimal notation, which is commonly found in engineering applications. Hexadecimal means ten (decimal) plus six (hexa), or combining the two to get base 16; two hexadecimal digits can then take on a total of 162 = 256 different values. We normally express numbers in decimal or base-10 notation, with ten digits ranging from 0 to 9. Hexadecimal has sixteen digits: the usual ten, ranging from 0 to 9, followed by six letters from A through F.
If you have ever written a web page in hypertext markup language (HTML), you might have tried to specify a color for a font or background in RGB. The most common method is to specify the brightness of each color from 0 (none) to 255 (brightest). Those are 256 different possible brightnesses for each color, because you have to remember to count zero, too! Another way of specifying numbers from zero to 255 is by using two–digit hexadecimal notation, which is commonly found in engineering applications. Hexadecimal means ten (decimal) plus six (hexa), or combining the two to get base 16; two hexadecimal digits can then take on a total of 162 = 256 different values. We normally express numbers in decimal or base-10 notation, with ten digits ranging from 0 to 9. Hexadecimal has sixteen digits: the usual ten, ranging from 0 to 9, followed by six letters from A through F.
The number 10 in base 10 is written as 0xA in hexadecimal, where the “0x” preceding the number tells you that it is in base 16 hexadecimal. The number 15 in base 10 is 0xF in hexadecimal. The number 7 in decimal is likewise 0x7 in hexadecimal. In hexadecimal when you reach the base-10 number 16 you have to add a new digit, just as you add a new digit in base 10 when you count past nine. The number 16 in base 10 is therefore 0x10 in hexadecimal.
When writing an RGB color for a webpage, there will usually be six hexadecimal digits listed: the first two digits for red, the next two for green, and the last two for blue. The color red is therefore a web color of 0xFF0000, green is 0x00FF00, and blue is 0x0000FF. White is the combination of all three colors, or 0xFFFFFF, whereas black is the absence of all three colors, or 0x000000. 
|
|
Digital (as opposed to analog) information can be stored reliably in computer memory. Digital files, such as images or music, can also be copied quickly, inexpensively, and without information loss; analog information degrades with each subsequent copy. On the other hand, many people have expressed concern about the security of digital personal information, the theft of copyrighted material, and the ease of accidental deletion.
|
How are the colors of the ink on a book page different from the colors on a TV screen? You see the light on the page reflected from the Sun or a light bulb. When printed, the red color on this page was created by a combination of pigments that reflect only magenta and yellow but absorb all the other colors within the white light shining on it. 
|
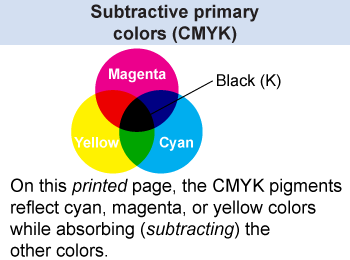 Printed illustrations use cyan, magenta, and yellow pigments in the ink to create any possible color. Professional printers realized that they could not obtain dark blacks with only cyan, magenta, and yellow, so they added a fourth ink—black or “K.” Cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (K) are known as subtractive primary colors (CMYK). This is called a subtractive primary color process because the pigments remove the light upon reflection, rather than being sources that emit light.
Printed illustrations use cyan, magenta, and yellow pigments in the ink to create any possible color. Professional printers realized that they could not obtain dark blacks with only cyan, magenta, and yellow, so they added a fourth ink—black or “K.” Cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (K) are known as subtractive primary colors (CMYK). This is called a subtractive primary color process because the pigments remove the light upon reflection, rather than being sources that emit light. 
|
How is additive primary color mixing different from mixing colors with paint?
 |
In light mixing, the colors combine to make lighter, brighter colors then the originals. All the colors combined make white.
In paint mixing, colors combine to form a color that is between the original colors in hue and brightness. All the colors mixed together will make brown or black, not white. 
|
| |
|

