|
 In heat transfer, conduction is the transfer of heat through or between materials by direct contact. Imagine a bar of copper and an identical size piece of wood. One end of each is immersed in boiling water and the other end is in your hand. If you did the experiment you could comfortably hold the wood but the copper would quickly become too hot to hold. The reason is that heat flows through copper 4,000 times more readily than heat flows through wood. This is why cooking spoons are typically made out of wood or plastic—or at least have wood or plastic handles—rather than being made entirely of metal.
In heat transfer, conduction is the transfer of heat through or between materials by direct contact. Imagine a bar of copper and an identical size piece of wood. One end of each is immersed in boiling water and the other end is in your hand. If you did the experiment you could comfortably hold the wood but the copper would quickly become too hot to hold. The reason is that heat flows through copper 4,000 times more readily than heat flows through wood. This is why cooking spoons are typically made out of wood or plastic—or at least have wood or plastic handles—rather than being made entirely of metal. 
|
In heat conduction, energy moves but not the matter itself. On the molecular level, hotter molecules have more kinetic energy and therefore more random motion. As neighboring molecules bump into each other they transfer kinetic energy. This transfer of intermolecular kinetic energy is the fundamental explanation for heat conduction. 
|
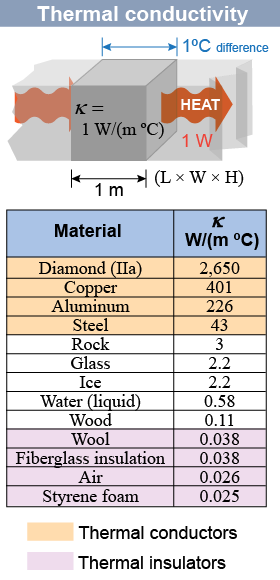
Different materials have very different abilities to conduct heat. The table (at right) compares the thermal conductivity of different materials. A thermal conductivity of one watt per meter per degree, or 1 W/(m ºC), means a 1ºC temperature difference across 1 m of length causes 1 W of heat to flow through 1 m2 of cross-sectional area. You can evaluate whether a material is a thermal conductor or insulator based on the value of its thermal conductivity κ listed in the table (at right). Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper, are classified as thermal conductors. Materials with low thermal conductivity, such as foam or air, are classified as thermal insulators. Other materials, such as glass, are intermediate heat conductors. 
| 
 |
Thermal conductivity varies by a factor of 100,000 from diamond, the best conductor among ordinary materials with κ = 2,650 W/(m ºC), to foam insulation, a good insulator with κ = 0.025 W/(m ºC). This variation results from the interaction of several factors: - The strength of bonds between neighboring atoms or molecules. The stronger the bonds, the higher the thermal conductivity. Diamond has very strong bonds between atoms and has one of the highest known thermal conductivities.
- The number of bonds or molecules per square meter (which correlates roughly with density). The best thermal conductors are dense metals and the best insulators are dilute gases.
- The material’s electrical conductivity. Good electrical conductors—such as metals—are also good thermal conductors. This effect is caused by the ability of free electrons to move thermal energy.
- The structure of a material. Solid glass has a thermal conductivity of 2.2 W/(m ºC) whereas the same glass spun into fiberglass insulation has a very low thermal conductivity of 0.038 W/(m ºC). The low value comes from many entrapped air spaces between fibers.

|
Think about touching a foam cup and a metal cup that have both been sitting on a table long enough to be at the same temperature as the room. The metal cup feels cold but the foam cup feels warm even though both are at the same temperature! What you feel is the difference in thermal conductivity. Metal conducts heat away from your skin much faster than foam. The skin touching the metal cup gets cooler, closer to room temperature, than the skin touching the foam cup. 
|
Which sentence most accurately uses the term thermal conductivity? - Boiling water burns exposed skin because of water’s high thermal conductivity.
- The highest thermal conductivity occurs when the difference in temperature between hot and cold is greatest.
- Metals typically have higher thermal conductivity than plastics; therefore, heat flows faster in metal than in plastic.
- Winter coats and sleeping bags use fiber filling (such as polyester) or feathers (such as down) to increase their thermal conductivity and thus keep your body warmer.
 |
Choice c is correct. Higher thermal conductivity means that heat flows more quickly for a given temperature difference. 
|

