- How many rad/s are equivalent to an angular velocity of 490°/min?
- 0.23 rad/s
- 0.05 rad/s
- 0.14 rad/s
- 0.19 rad/s
- Tomás faces due north. He then turns counterclockwise until he is facing due east. How many radians did he turn?
- 1⁄2 π rad
- 6.28 rad
- 3⁄2 π rad
- 0.75 rad
- What is the linear velocity of a rolling wheel with a diameter of 4 m, rotating at 2π rad/s?
- 6.3 m/s
- 12.6 m/s
- 25.1 m/s
- 4.0 m/s
- A rolling ball is rotating at 5 rad/s. If the ball has a radius of 0.5 m, how far does it travel in 3 s?
- 30 m
- 0.83 m
- 7.5 m
- 45 m
- A wheel on a watermill turns halfway every 5 s. What is the wheel’s angular velocity?
- 5π rad/s
- π/5 rad/s
- 2.5 rad/s
- 25 rad/s
- Assume 1,200 N is the maximum friction force between the tires and the ground for an 1,100 kg car. Without skidding, how fast can the car go around a curve with a radius of 200 m?
- 25 m/s
- 20 m/s
- 15 m/s
- 10 m/s
- Say you and your friend each have a mass of 80 kg. You are floating motionless in space, 1.5 m apart from each other. How much gravitational force is there between you?
- 2.9×10−6 N
- 1.9×10−7 N
- 2.4×10−9 N
- 3.6×10−9 N
| | - What is the gravitational force between the proton in a hydrogen atom (mass of 1.7×10−27 kg) and the electron in a hydrogen atom (mass of 9.1×10−31 kg)? Assume they are 2.5×10−11 m apart.
- 1.6×10−46 N
- 3.5×10−46 N
- 6.4×10−46 N
- 8.9×10−46 N
- How many degrees are equal to 8 radians.
- 386°
- 424°
- 342°
- 458°
- What is your centripetal acceleration when you run at 11 m/s around the curve of an Olympic track, which has a radius of 36.5 m?
- 0.30 m/s2
- 1.2 m/s2
- 3.3 m/s2
- 2.4 m/s2
- At what speed would a 1 kg satellite orbit if it were 1,400 km above the Earth’s surface? (Earth has a mass of 6.0×1024 kg and a radius of 6,400 km.)
- 7,200 m/s
- 230,000 m/s
- 130,000 m/s
- 68,000 m/s
- Which of the following best explains why Mars takes longer than Earth to orbit the Sun.
- Mars has farther to go (its orbit is larger).
- Mars orbits more slowly (its speed is lower).
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
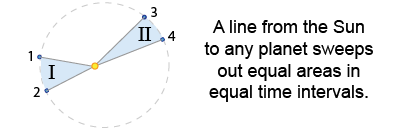
- One planet’s elliptical orbit is shown here, along with a statement of Kepler’s second law. The time taken to go from 1 to 2 equals the time to go from 3 to 4. Which of the following best completes the following sentence?
The planet is closer to the Sun in _______ and moves faster in _______.
- Stage I, Stage I
- Stage I, Stage II
- Stage II, Stage II
- Stage II, Stage I
|

