- Habin took a wave motion rope and waved it sideways repeatedly to create waves. What kind of waves did he create, transverse, longitudinal, or a pulse?
- Varujian took a wave motion rope and waved it sideways once. What kind of wave did he create, transverse, longitudinal, or a pulse?
- Chakra took a Slinky® spring and repeatedly compressed and extended one end to create wave pulses. Did he create transverse or longitudinal waves?
 Sven measured the distance along a wave for three complete oscillations. If he wants to know the wavelength, should he multiply or divide his number by 3? Sven measured the distance along a wave for three complete oscillations. If he wants to know the wavelength, should he multiply or divide his number by 3?
 Describe how to create (a) circular waves and (b) plane waves in a bathtub full of water. Describe how to create (a) circular waves and (b) plane waves in a bathtub full of water.
 Draw a wave on a position–time graph and label the amplitude and period. Draw a wave on a position–time graph and label the amplitude and period.
 Is a wave motion rope or a Slinky® spring the best choice of equipment to create both a transverse and a longitudinal wave? Is a wave motion rope or a Slinky® spring the best choice of equipment to create both a transverse and a longitudinal wave?
- Which sentence best expresses in words the meaning of the equation below?
- The velocity of a wave equals its amplitude multiplied by its wavelength.
- The velocity of a wave is equal to the ratio of its wavelength to its frequency.
- Amplitude multiplied by frequency equals the wavelength.
- The velocity of a wave equals its wavelength times its frequency.
 You are given a long piece of rope with one end tied to the wall. Describe how you can create (a) a wave pulse and (b) a standing wave with the rope. You are given a long piece of rope with one end tied to the wall. Describe how you can create (a) a wave pulse and (b) a standing wave with the rope.
 Imagine you are standing 100 m above the bottom of a valley on a rope bridge that is oscillating with a standing wave. Would you prefer to stand in a location that is a node or an antinode? Why? Imagine you are standing 100 m above the bottom of a valley on a rope bridge that is oscillating with a standing wave. Would you prefer to stand in a location that is a node or an antinode? Why?
 Imagine you are designing an amusement park ride using a rope bridge that is oscillating with a standing wave. Do you think that customers would prefer to stand in a location that is a node or an antinode? Why? Imagine you are designing an amusement park ride using a rope bridge that is oscillating with a standing wave. Do you think that customers would prefer to stand in a location that is a node or an antinode? Why?
| |
- Explain how the diffraction of waves plays a role in radio transmission and cellphone service.
- Describe how refraction is used in optical imaging and ultrasound imaging.
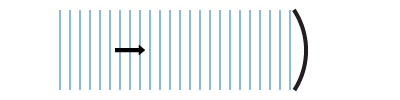
 A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank and a curved surface. Draw how plane waves reflect off of the curved surface in the illustration shown. A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank and a curved surface. Draw how plane waves reflect off of the curved surface in the illustration shown.
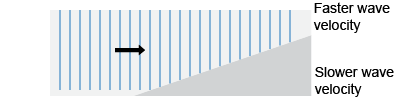
 A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank in which the waves refract from one medium into another in which the wave velocity is lower. Draw how plane waves refract from the boundary between two materials as shown in the illustration. A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank in which the waves refract from one medium into another in which the wave velocity is lower. Draw how plane waves refract from the boundary between two materials as shown in the illustration.
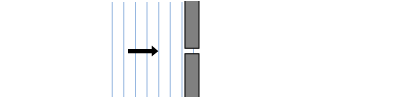
 A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank in which the waves diffract after passing through a small opening. Draw how plane waves diffract in the illustration shown. A student was conducting an investigation with a wave tank in which the waves diffract after passing through a small opening. Draw how plane waves diffract in the illustration shown.
 What wave behavior explains why you can hear the radio playing in another room even though you cannot see it? What wave behavior explains why you can hear the radio playing in another room even though you cannot see it?
 A person who shouts while hiking in a canyon is likely to hear an echo. What wave behavior explains this phenomenon? A person who shouts while hiking in a canyon is likely to hear an echo. What wave behavior explains this phenomenon?
- Ocean waves entering the shallow water surrounding an island will bend so that the incoming crests are roughly parallel to the shore rather than at right angles to it. What wave behavior explains this phenomena?
 Jack measured the wavelength of a wave using successive crests. Jill measured the wavelength using successive troughs. Who will measure the wavelength correctly? Jack measured the wavelength of a wave using successive crests. Jill measured the wavelength using successive troughs. Who will measure the wavelength correctly?
 Does a wave propagate parallel or perpendicular to its wavefront? Does a wave propagate parallel or perpendicular to its wavefront?
|

